Asymmetric regulation of quorum-sensing receptors drives autoinducer-specific gene expression programs in Vibrio cholerae
- PMID: 28552952
- PMCID: PMC5467912
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006826
Asymmetric regulation of quorum-sensing receptors drives autoinducer-specific gene expression programs in Vibrio cholerae
Abstract
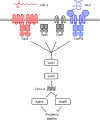
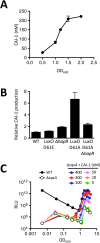
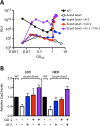
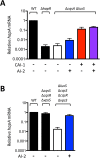
Quorum sensing (QS) is a mechanism of chemical communication that bacteria use to monitor cell-population density and coordinate group behaviors. QS relies on the production, detection, and group-wide response to extracellular signal molecules called autoinducers. Vibrio cholerae employs parallel QS circuits that converge into a shared signaling pathway. At high cell density, the CqsS and LuxPQ QS receptors detect the intra-genus and inter-species autoinducers CAI-1 and AI-2, respectively, to repress virulence factor production and biofilm formation. We show that positive feedback, mediated by the QS pathway, increases CqsS but not LuxQ levels during the transition into QS-mode, which amplifies the CAI-1 input into the pathway relative to the AI-2 input. Asymmetric feedback on CqsS enables responses exclusively to the CAI-1 autoinducer. Because CqsS exhibits the dominant QS signaling role in V. cholerae, agonism of CqsS with synthetic compounds could be used to control pathogenicity and host dispersal. We identify nine compounds that share no structural similarity to CAI-1, yet potently agonize CqsS via inhibition of CqsS autokinase activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Papenfort K, Bassler BL. Quorum sensing signal-response systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016;14(9):576–88. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.89 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Higgins DA, Pomianek ME, Kraml CM, Taylor RK, Semmelhack MF, Bassler BL. The major Vibrio cholerae autoinducer and its role in virulence factor production. Nature. 2007;450(7171):883–6. doi: 10.1038/nature06284 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Schauder S, Potier N, Van Dorsselaer A, Pelczer I, Bassler BL, et al. Structural identification of a bacterial quorum-sensing signal containing boron. Nature. 2002;415(s):545–9. - PubMed
-
- Wei Y, Perez LJ, Ng W-L, Semmelhack MF, Bassler BL. Mechanism of Vibrio cholerae autoinducer-1 biosynthesis. ACS Chem Biol. 2011;6(4):356–65. doi: 10.1021/cb1003652 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

