Skeletal and Appendage Diversity as Design Elements in the Synthesis of a Discovery Library of Nonaromatic Polycyclic 5-Iminooxazolidin-2-ones, Hydantoins, and Acylureas
- PMID: 28553003
- PMCID: PMC5444204
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tet.2008.02.033
Skeletal and Appendage Diversity as Design Elements in the Synthesis of a Discovery Library of Nonaromatic Polycyclic 5-Iminooxazolidin-2-ones, Hydantoins, and Acylureas
Abstract
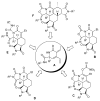
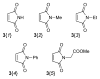
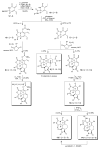
Amino acid-derived cross-conjugated trienes were used as a starting point for the synthesis of a discovery library of over 200 polycyclic 5-iminooxazolidin-2-ones, hydantoins, and acylureas. The main feature of this library synthesis is a triple branching strategy which provides efficient access to five skeletally diverse scaffolds. In addition, four sets of building blocks were applied in both a front end and a back end diversification strategy. Multiple fused rings were obtained by cyclization of diamides with phosgene and stereoselective Diels-Alder reactions with maleimides. The 5-iminooxazolidin-2-one scaffold was rearranged into the isomeric hydantoin scaffold through a sequence of ring opening and ring closing reactions.
Keywords: Appendage Diversity; Diels Alder Reaction; Library Design; Polycycles; Skeletal Diversity.
Figures
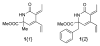
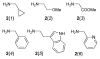
References
-
- Webb TR. Curr Opin Drug Disc Dev. 2005;8:303–308. - PubMed
-
- Schreiber SL. Science. 2000;287:1964–1969. - PubMed
- Burke MD, Lalic G. Chem Biol. 2002;9:535–541. - PubMed
- Spring DR. Org Biomol Chem. 2003;1:3867–3870. - PubMed
- Burke MD, Schreiber SL. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2004;43:46–58. - PubMed
- Taylor SJ, Taylor AM, Schreiber SL. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2004;43:1681–1685. - PubMed
-
- Tan DS. Nat Chem Biol. 2005;1:74–84. - PubMed
-
- Selzer P, Roth HJ, Ertl P, Schuffenhauer A. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2005;9:310–316. - PubMed
-
- Liao Y, Hu Y, Wu J, Zhu Q, Donovan M, Fathi R, Yang Z. Curr Med Chem. 2003;10:2285–2316. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
