Phosphonium ionic liquids as extractants for recovery of ruthenium(III) from acidic aqueous solutions
- PMID: 28553005
- PMCID: PMC5425505
- DOI: 10.1007/s11696-016-0027-1
Phosphonium ionic liquids as extractants for recovery of ruthenium(III) from acidic aqueous solutions
Abstract
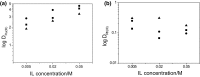
The aim of this work is to investigate extraction of ruthenium(III) from acidic aqueous solutions with phosphonium ionic liquids such as trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium chloride (Cyphos IL 101), trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl)phosphinate (Cyphos IL 104) and tributyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium chloride (Cyphos IL 167) as extractants. The influence of HCl content in the feed solutions on extraction of Ru(III) was investigated. The research was performed for model solutions containing Ru(III) and a mixture of waste solutions containing Ru(III) and Rh(III). In addition, investigation of the type of extractant and its concentration in the organic phase on extraction of Ru(III) was carried out. Co-extraction of protons to the organic phase was determined. To the best of our knowledge, the extraction of Ru(III) with Cyphos IL 167 (tributyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium chloride) as an extractant has not yet been described in the scientific literature.
Keywords: Cyphos IL 101; Cyphos IL 104; Cyphos IL 167; Liquid–liquid extraction; Phosphonium ionic liquid; Rhodium(III); Ruthenium(III).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Application of Phosphonium Ionic Liquids as Ion Carriers in Polymer Inclusion Membranes (PIMs) for Separation of Cadmium(II) and Copper(II) from Aqueous Solutions.J Solution Chem. 2015;44(12):2431-2447. doi: 10.1007/s10953-015-0413-2. Epub 2015 Nov 12. J Solution Chem. 2015. PMID: 26659810 Free PMC article.
-
Extraction of Gold(III) from Hydrochloric Acid Solutions with a PVC-based Polymer Inclusion Membrane (PIM) Containing Cyphos(®) IL 104.Membranes (Basel). 2015 Dec 8;5(4):903-14. doi: 10.3390/membranes5040903. Membranes (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26670259 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid-liquid extraction of europium(III) and other trivalent rare-earth ions using a non-fluorinated functionalized ionic liquid.Dalton Trans. 2014 Jan 28;43(4):1862-72. doi: 10.1039/c3dt52285g. Dalton Trans. 2014. PMID: 24257814
-
Recovery of pure germanium oxide from Zener diodes using a recyclable ionic liquid Cyphos IL 104.J Environ Manage. 2020 Dec 15;276:111218. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111218. Epub 2020 Sep 1. J Environ Manage. 2020. PMID: 32882518
-
Scandium Recovery Methods from Mining, Metallurgical Extractive Industries, and Industrial Wastes.Materials (Basel). 2022 Mar 23;15(7):2376. doi: 10.3390/ma15072376. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35407709 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation on Water Vapor Adsorption of Silica-Phosphonium Ionic Liquids Hybrid Material.Materials (Basel). 2019 Jun 1;12(11):1782. doi: 10.3390/ma12111782. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31159368 Free PMC article.
-
Amide-functionalised phosphonium-based ionic liquids as ligands for rhodium(iii) extraction.RSC Adv. 2021 Mar 2;11(16):9386-9394. doi: 10.1039/d1ra00489a. eCollection 2021 Mar 1. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35423411 Free PMC article.
-
Recovery of Palladium(II) and Platinum(IV) in Novel Extraction Systems.Materials (Basel). 2021 Jan 8;14(2):285. doi: 10.3390/ma14020285. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33429884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott AP, Frisch G, Hartley J, Ryder KS. Processing of metals and metal oxides using ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2011;13:471–481. doi: 10.1039/c0gc00716a. - DOI
-
- Afzaletdinova NG, Ryamova LM, Murinov YI. Extraction of chlororuthenium(III) complexes by triazole derivatives from hydrochloric acid solutions. Russ J Inorg Chem. 2007;52:800–805. doi: 10.1134/S0036023607050269. - DOI
-
- Baczyńska M, Regel-Rosocka M. Phosphonium ionic liquids as carriers of metal ions. Przemysł Chemiczny. 2013;92(9):1574–1576.
-
- Baczyńska M, Rzelewska M, Regel-Rosocka M, Wiśniewski M. Transport of iron ions from chloride solutions using cellulose triacetate matrix inclusion membranes with an ionic liquid carrier. Chem Pap. 2016;70(2):172–179.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
