The metal nanoparticle-induced inflammatory response is regulated by SIRT1 through NF-κB deacetylation in aseptic loosening
- PMID: 28553103
- PMCID: PMC5439723
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S124661
The metal nanoparticle-induced inflammatory response is regulated by SIRT1 through NF-κB deacetylation in aseptic loosening
Abstract
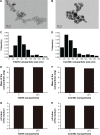
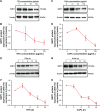
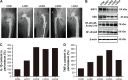
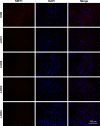
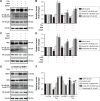
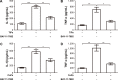
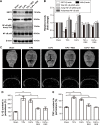
Aseptic loosening is the most common cause of total hip arthroplasty (THA) failure, and osteolysis induced by wear particles plays a major role in aseptic loosening. Various pathways in multiple cell types contribute to the pathogenesis of osteolysis, but the role of Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), which can regulate inflammatory responses through its deacetylation, has never been investigated. We hypothesized that the downregulation of SIRT1 in macrophages induced by metal nanoparticles was one of the reasons for osteolysis in THA failure. In this study, the expression of SIRT1 was examined in macrophages stimulated with metal nanoparticles from materials used in prosthetics and in specimens from patients suffering from aseptic loosening. To address whether SIRT1 downregulation triggers these inflammatory responses, the effects of the SIRT1 activator resveratrol on the expression of inflammatory cytokines in metal nanoparticle-stimulated macrophages were tested. The results demonstrated that SIRT1 expression was significantly downregulated in metal nanoparticle-stimulated macrophages and clinical specimens of prosthesis loosening. Pharmacological activation of SIRT1 dramatically reduced the particle-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines in vitro and osteolysis in vivo. Furthermore, SIRT1 regulated particle-induced inflammatory responses through nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) acetylation. Thus, the results of this study suggest that SIRT1 plays a key role in metal nanoparticle-induced inflammatory responses and that targeting the SIRT1 pathway may lead to novel therapeutic approaches for the treatment of aseptic prosthesis loosening.
Keywords: NF-κB; SIRT1; aseptic loosening; inflammatory response; metal nanoparticle.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures




Similar articles
-
SIRT1 protects osteoblasts against particle-induced inflammatory responses and apoptosis in aseptic prosthesis loosening.Acta Biomater. 2017 Feb;49:541-554. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.11.051. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 27890623
-
Particle-induced osteolysis mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress in prosthesis loosening.Biomaterials. 2013 Apr;34(11):2611-23. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.01.025. Epub 2013 Jan 21. Biomaterials. 2013. PMID: 23347837
-
Hydrogen sulfide protects against particle-induced inflammatory response and osteolysis via SIRT1 pathway in prosthesis loosening.FASEB J. 2020 Mar;34(3):3743-3754. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900393RR. Epub 2020 Jan 14. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 31943384
-
Involvement of NF-κB/NLRP3 axis in the progression of aseptic loosening of total joint arthroplasties: a review of molecular mechanisms.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022 Jul;395(7):757-767. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02232-4. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35377011 Review.
-
Mechanism of regulating macrophages/osteoclasts in attenuating wear particle-induced aseptic osteolysis.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 4;14:1274679. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1274679. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37860014 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glycyrrhizin mitigates inflammatory bone loss and promotes expression of senescence-protective sirtuins in an aging mouse model of periprosthetic osteolysis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jun;138:111503. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111503. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33770668 Free PMC article.
-
Human Breast Milk-Derived Exosomal miR-148a-3p Protects Against Necrotizing Enterocolitis by Regulating p53 and Sirtuin 1.Inflammation. 2022 Jun;45(3):1254-1268. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01618-5. Epub 2022 Jan 29. Inflammation. 2022. PMID: 35091894
-
Reduction of Silent Information Regulator 1 Activates Interleukin-33/ST2 Signaling and Contributes to Neuropathic Pain Induced by Spared Nerve Injury in Rats.Front Mol Neurosci. 2020 Feb 12;13:17. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00017. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32116550 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol reduces the progression of titanium particle-induced osteolysis via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Oct;22(4):1119. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10553. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34504573 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1-SIRT7 in Diabetic Kidney Disease: Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 May 13;13:801303. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.801303. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35634495 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Prokopovich P. Interactions between mammalian cells and nano- or micro-sized wear particles: physico-chemical views against biological approaches. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2014;213:36–47. - PubMed
-
- Deng Z, Wang Z, Jin J, et al. SIRT1 protects osteoblasts against particle-induced inflammatory responses and apoptosis in aseptic prosthesis loosening. Acta Biomater. 2017;49:541–554. - PubMed
-
- Purdue PE, Koulouvaris P, Potter HG, Nestor BJ, Sculco TP. The cellular and molecular biology of periprosthetic osteolysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;454:251–261. - PubMed
-
- Wang R, Wang Z, Ma Y, et al. Particle-induced osteolysis mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress in prosthesis loosening. Biomaterials. 2013;34(11):2611–2623. - PubMed
-
- Gallo J, Raska M, Mrazek F, Petrek M. Bone remodeling, particle disease and individual susceptibility to periprosthetic osteolysis. Physiol Res. 2008;57(3):339–349. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

