Cadmium Telluride Semiconductor Detector for Improved Spatial and Energy Resolution Radioisotopic Imaging
- PMID: 28553175
- PMCID: PMC5436314
- DOI: 10.4103/1450-1147.203079
Cadmium Telluride Semiconductor Detector for Improved Spatial and Energy Resolution Radioisotopic Imaging
Abstract
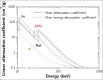
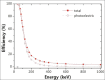
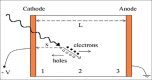
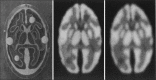
The detector in single-photon emission computed tomography has played a key role in the quality of the images. Over the past few decades, developments in semiconductor detector technology provided an appropriate substitution for scintillation detectors in terms of high sensitivity, better energy resolution, and also high spatial resolution. One of the considered detectors is cadmium telluride (CdTe). The purpose of this paper is to review the CdTe semiconductor detector used in preclinical studies, small organ and small animal imaging, also research in nuclear medicine and other medical imaging modalities by a complete inspect on the material characteristics, irradiation principles, applications, and epitaxial growth method.
Keywords: Cadmium telluride; image quality; radiation detector; semiconductor; single-photon emission computed tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Milbrath BD, Peurrung AJ, Bliss M, Weber WJ. Radiation detector materials: An overview. J Mater Res. 2008;23:2561–81.
-
- Heller S, Zanzonico P. Nuclear probes and intraoperative gamma cameras. Semin Nucl Med. 2011;41:166–81. - PubMed
-
- Weber MJ. Inorganic scintillators: Today and tomorrow. J Lumin. 2002;100:35–45.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

