Transcriptome Analysis of Floral Buds Deciphered an Irregular Course of Meiosis in Polyploid Brassica rapa
- PMID: 28553302
- PMCID: PMC5427127
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00768
Transcriptome Analysis of Floral Buds Deciphered an Irregular Course of Meiosis in Polyploid Brassica rapa
Abstract
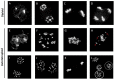
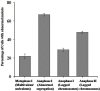
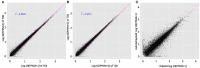
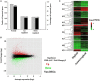
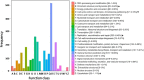
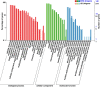
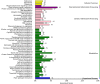
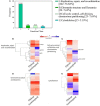
Polyploidy is a fundamental process in plant evolution. Understanding the polyploidy-associated effects on plant reproduction is essential for polyploid breeding program. In the present study, our cytological analysis firstly demonstrated that an overall course of meiosis was apparently distorted in the synthetic polyploid Brassica rapa in comparison with its diploid progenitor. To elucidate genetic basis of this irregular meiosis at a molecular level, the comparative RNA-seq analysis was further used to investigate differential genetic regulation of developing floral buds identified at meiosis between autotetraploid and diploid B. rapa. In total, compared to its diploid counterparts, among all 40,927 expressed genes revealed, 4,601 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified in the floral buds of autotetraploid B. rapa, among which 288 DEGs annotated were involved in meiosis. Notably, DMC1 identified as one previously known meiosis-specific gene involved in inter-homologous chromosome dependent repair of DNA double stranded breaks (DSBs), was significantly down-regulated in autotetraploid B. rapa, which presumably contributed to abnormal progression during meiosis I. Although certain DEGs associated with RNA helicase, cell cycling, and somatic DNA repair were up-regulated after genome duplication, genes associated with meiotic DSB repair were significantly down-regulated. Furthermore, the expression of randomly selected DEGs by RNA-seq analysis was confirmed by quantitative real-time PCR analysis in both B. rapa and Arabidopsis thaliana. Our results firstly account for adverse effects of polyploidy on an entire course of meiosis at both cytological and transcriptomic levels, and allow for a comprehensive understanding of the uniformity and differences in the transcriptome of floral buds at meiosis between diploid and polyploid B. rapa as well.
Keywords: Brassica rapa; RNA-seq analysis; floral buds; meiosis; polyploidy; transcriptome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis revealed differential gene expression in multiple signaling pathways at flowering in polyploid Brassica rapa.Cell Biosci. 2021 Jan 12;11(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00528-1. Cell Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33436051 Free PMC article.
-
Cytological and proteomic analyses of floral buds reveal an altered atlas of meiosis in autopolyploid Brassica rapa.Cell Biosci. 2019 Jun 17;9:49. doi: 10.1186/s13578-019-0313-z. eCollection 2019. Cell Biosci. 2019. PMID: 31236208 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of spatiotemporal gene expression patterns during floral organ development in Brassica rapa.Mol Genet Genomics. 2019 Dec;294(6):1403-1420. doi: 10.1007/s00438-019-01585-5. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Mol Genet Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31222475
-
Chromosome 'speed dating' during meiosis of polyploid Brassica hybrids and haploids.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2008;120(3-4):331-8. doi: 10.1159/000121082. Epub 2008 May 23. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2008. PMID: 18504362 Review.
-
Genetic regulation of meiosis in polyploid species: new insights into an old question.New Phytol. 2010 Apr;186(1):29-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03084.x. Epub 2009 Nov 11. New Phytol. 2010. PMID: 19912546 Review.
Cited by
-
Physiological and transcriptome analyses of Opisthopappus taihangensis in response to drought stress.Cell Biosci. 2019 Jul 4;9:56. doi: 10.1186/s13578-019-0318-7. eCollection 2019. Cell Biosci. 2019. PMID: 31312427 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of drought resistance and transcriptome analysis for the identification of drought-responsive genes in Iris germanica.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 11;11(1):16308. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95633-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34381085 Free PMC article.
-
Non-homologous chromosome pairing during meiosis in haploid Brassica rapa.Plant Cell Rep. 2021 Dec;40(12):2421-2434. doi: 10.1007/s00299-021-02786-2. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Plant Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34542669
-
Effect of paleopolyploidy and allopolyploidy on gene expression in banana.BMC Genomics. 2019 Mar 27;20(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5618-0. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30917780 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis revealed differential gene expression in multiple signaling pathways at flowering in polyploid Brassica rapa.Cell Biosci. 2021 Jan 12;11(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00528-1. Cell Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33436051 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bottley A. (2014). Epigenetic variation amongst polyploidy crop species, in Epigenetics in Plants of Agronomic Importance: Fundamentals and Applications, eds Alvarez-Venegas R., De la Peña C., Casas-Mollano J. A. (Springer International Publishing Switzerland; ), 33–46.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

