Bone Regeneration Induced by Bone Porcine Block with Bone Marrow Stromal Stem Cells in a Minipig Model of Mandibular "Critical Size" Defect
- PMID: 28553359
- PMCID: PMC5434233
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/9082869
Bone Regeneration Induced by Bone Porcine Block with Bone Marrow Stromal Stem Cells in a Minipig Model of Mandibular "Critical Size" Defect
Abstract
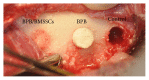
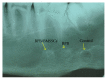
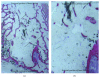
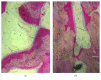
Introduction. Adding stem cells to biodegradable scaffolds to enhance bone regeneration is a valuable option. Different kinds of stem cells with osteoblastic activity were tested, such as bone marrow stromal stem cells (BMSSCs). Aim. To assess a correct protocol for osteogenic stem cell differentiation, so BMSSCs were seeded on a bone porcine block (BPB). Materials and Methods. Bone marrow from six minipigs was extracted from tibiae and humeri and treated to isolate BMSSCs. After seeding on BPB, critical-size defects were created on each mandible of the minipigs and implanted with BPB and BPB/BMSSCs. After three months, histomorphometric analysis was performed. Results. Histomorphometric analysis provided percentages of the three groups. Tissues present in control defects were 23 ± 2% lamellar bone, 28 ± 1% woven bone, and 56 ± 4% marrow spaces; in BPB defects were 20 ± 5% BPB, 32 ± 2% lamellar bone, 24 ± 1% woven bone, and 28 ± 2% marrow spaces; in BPB/BMSSCs defects were 17 ± 4% BPB/BMSSCs, 42 ± 2% lamellar bone, 12 ± 1% woven bone, and 22 ± 3% marrow spaces. Conclusion. BPB used as a scaffold to induce bone regeneration may benefit from the addition of BDPSCs in the tissue-engineered constructs.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bone regeneration in minipigs via calcium phosphate cement scaffold delivering autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018 Feb;12(2):e937-e948. doi: 10.1002/term.2416. Epub 2017 Jun 2. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018. PMID: 28102000
-
Ectopic osteogenesis and chondrogenesis of bone marrow stromal stem cells in alginate system.Cell Biol Int. 2007 Aug;31(8):776-83. doi: 10.1016/j.cellbi.2007.01.011. Epub 2007 Jan 21. Cell Biol Int. 2007. PMID: 17324591
-
Reconstruction of mandibular defects with autologous tissue-engineered bone.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004 May;62(5):601-6. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2003.11.010. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004. PMID: 15122567
-
Bone formation by human postnatal bone marrow stromal stem cells is enhanced by telomerase expression.Nat Biotechnol. 2002 Jun;20(6):587-91. doi: 10.1038/nbt0602-587. Nat Biotechnol. 2002. PMID: 12042862
-
Skeletal stem cells in regenerative medicine.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2005;67:305-23. doi: 10.1016/S0070-2153(05)67010-X. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2005. PMID: 15949539 Review.
Cited by
-
Dental Pulp Stem Cells on Implant Surface: An In Vitro Study.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Mar 23;2021:3582342. doi: 10.1155/2021/3582342. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33834063 Free PMC article.
-
Self-assembled microtissues loaded with osteogenic MSCs for in vivo bone regeneration.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Dec 12;10:1069804. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1069804. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36578514 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Blocks for Bone Regeneration: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 28;20(17):4221. doi: 10.3390/ijms20174221. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31466409 Free PMC article.
-
The 15-Months Clinical Experience of SARS-CoV-2: A Literature Review of Therapies and Adjuvants.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 May 31;10(6):881. doi: 10.3390/antiox10060881. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34072708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P53 negatively regulates the osteogenic differentiation in jaw bone marrow MSCs derived from diabetic osteoporosis.Heliyon. 2023 Apr 3;9(4):e15188. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15188. eCollection 2023 Apr. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37096002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friedenstein A. Stromal mechanisms of bone marrow: cloning in vitro and retransplantation in vivo. Haematology and Blood Transfusion. 1980;25:19–29. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

