A Single-Institution Analysis of 126 Patients Treated with Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases
- PMID: 28553615
- PMCID: PMC5427066
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00090
A Single-Institution Analysis of 126 Patients Treated with Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases
Abstract
Background: The objective of this study was to report our institutional experience with Gamma Knife® Radiosurgery (GKRS) in the treatment of patients with brain metastases.
Methods: Retrospectively collected demographic and clinical data on 126 patients with intracranial metastases were reviewed. The patients in our study underwent GKRS at Vidant Medical Center between 2009 and 2014. Kaplan-Meier curves were used to compare survival based on clinical characteristics for univariate analysis, and a Cox proportional hazards model was used for multivariate analysis.
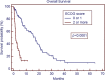
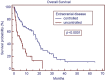
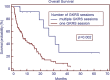
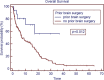
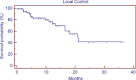
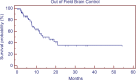
Results: The median age of the patient population was 62 years. Medicare patients constituted 51% of our patient cohort and Medicaid patients 15%. The most common tumor histologies were non-small cell lung cancer (50%), breast cancer (12.7%), and melanoma (11.9%). The median overall survival time for all patients was 5.8 months. Patients with breast cancer had the longest median survival time of 9.15 months, while patients with melanoma had the shortest median survival time of 2.86 months. On univariate analysis, the following factors were predictors for improved overall survival, ECOG score 0 or 1 vs. 2 or greater (17.0 vs. 1.8 months, p < 0.001), controlled extracranial disease vs. progressive extracranial disease (17.4 vs. 4.6 months, p = 0.0001), recursive partitioning analysis Stage I vs. II-III (18.2 vs. 6.2 months, p < 0.007), multiple GKRS treatments (p = 0.002), prior brain metastasectomy (p = 0.012), and prior chemotherapy (p = 0.021). Age, ethnicity, gender, previous external beam radiation therapy, number of brain metastases, and hemorrhagic vs. non-hemorrhagic tumors were not predictors of longer median survival time. Number of metastatic brain lesions of 1-3 vs. ≥4 (p = 0.051) and insurance status of Medicare/Medicaid vs. commercial insurance approached significance (13.7 vs. 6.8 months, p = 0.08). On multivariate analysis, ECOG performance status 0-1 (p < 0.001), multiple GKRS treatments (p = 0.003), and control of extracranial disease (p = 0.001) remained significant predictors of survival.
Conclusion: ECOG score, control of extracranial disease, and multiple GKRS treatments are predictors of longer median survival following GKRS in our patient population. GKRS is an effective treatment for brain metastases, but these factors may be considered in patient selection for GKRS.
Keywords: Gamma Knife; brain neoplasms; radiosurgery; stereotactic radiosurgery; underinsured.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gamma Knife radiosurgery for brain metastases from pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: a Japanese multi-institutional cooperative study (JLGK1401).J Neurosurg. 2016 Dec;125(Suppl 1):11-17. doi: 10.3171/2016.7.GKS161459. J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 27903179
-
Clinical outcomes in patients with brain metastases from breast cancer treated with single-session radiosurgery or whole brain radiotherapy.J Neurosurg. 2016 Dec;125(Suppl 1):26-30. doi: 10.3171/2016.7.GKS161541. J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 27903186
-
Gamma Knife radiosurgery for intracranial benign meningiomas: follow-up outcome in 130 patients.Neurosurg Focus. 2019 Jun 1;46(6):E7. doi: 10.3171/2019.3.FOCUS1956. Neurosurg Focus. 2019. PMID: 31153153
-
Outcomes of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases From Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Rearrangement-Positive and EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cureus. 2021 Dec 13;13(12):e20398. doi: 10.7759/cureus.20398. eCollection 2021 Dec. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 35047245 Free PMC article.
-
Neurosurgical management of perineural metastases: A case series and review of the literature.Surg Neurol Int. 2020 Jul 25;11:206. doi: 10.25259/SNI_146_2020. eCollection 2020. Surg Neurol Int. 2020. PMID: 32874709 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adjuvant radiotherapy and outcomes of presumed hemorrhagic melanoma brain metastases without malignant cells.Surg Neurol Int. 2018 Jul 26;9:146. doi: 10.4103/sni.sni_140_18. eCollection 2018. Surg Neurol Int. 2018. PMID: 30105140 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Metastases in Adults: A Five-Year Observational Study From King Abdulaziz Medical City.Cureus. 2022 Nov 7;14(11):e31197. doi: 10.7759/cureus.31197. eCollection 2022 Nov. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36505114 Free PMC article.
-
Local failure after stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for intracranial metastasis: analysis from a cooperative, prospective national registry.J Neurooncol. 2021 Apr;152(2):299-311. doi: 10.1007/s11060-021-03698-7. Epub 2021 Jan 22. J Neurooncol. 2021. PMID: 33481148
-
Linac-Based Radiosurgery for Patients With Brain Oligometastases From a Breast Primary, in the Trastuzumab Era-Impact of Tumor Phenotype and Prescribed SRS Dose.Front Oncol. 2019 May 28;9:377. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00377. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31192116 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

