Alcoholic Fractions F5 and F6 from Withania somnifera Leaves Show a Potent Antileishmanial and Immunomodulatory Activities to Control Experimental Visceral Leishmaniasis
- PMID: 28553635
- PMCID: PMC5427131
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2017.00055
Alcoholic Fractions F5 and F6 from Withania somnifera Leaves Show a Potent Antileishmanial and Immunomodulatory Activities to Control Experimental Visceral Leishmaniasis
Abstract
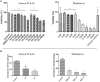
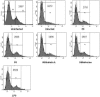
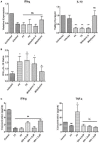
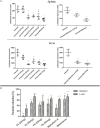
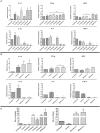
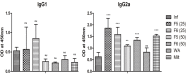
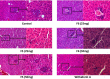
Visceral leishmaniasis (VL) causes fatal life-threatening disease, if left untreated. The current drugs have various limitations; hence, natural products from medicinal plants are being focused in search of new drugs to treat leishmaniasis. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the antileishmanial and immunomodulatory activities of F5 and F6 alcoholic fractions from Withania somnifera leaves and purified withaferin-A in Leishmania donovani-infected peritoneal macrophages and BALB/c mice. We observed that F5 (15 µg/mL), F6 (10 µg/mL), and withaferin-A (1.5 µM) reduce amastigote count in peritoneal macrophages and induce reactive oxygen species and significant decrease in IL-10 mRNA expression compared to control upon treatment. Subsequently, in vivo study mice were treated with F5 (25 and 50 mg/kg b.wt.), F6 (25 and 50 mg/kg b.wt.) orally, and withaferin-A (2 mg/kg b.wt.) intraperitoneally for 10 consecutive days and a drastic reduction in parasite burden in both spleen and liver were observed. The treatment resulted in the reduction in IL-10, IL-4, and TGF-β mRNA expression and a significant increase in IFN-γ/IL-10 expression ratio in the treated group compared to control. The humoral response of these alcoholic fractions and withaferin-A shows increased IgG2a levels when compared with IgG1 in treated mice. Taken together, our result concludes that withanolides in alcoholic fractions demonstrate a potent antileishmanial and immunomodulatory activities in experimental VL.
Keywords: IL-10; Withania somnifera; peritoneal mouse macrophages; visceral leishmaniasis; withaferin-A.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Magnitude of the Problem. (2005). Available from: http://www.who.int/leishmaniasis/burden/magnitude/burden_magnitude/en/in...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

