Cardiac rehabilitation in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: can its failure be predicted?
- PMID: 28553755
- PMCID: PMC5933644
- DOI: 10.1177/1753944717706845
Cardiac rehabilitation in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: can its failure be predicted?
Abstract
Background: The prognosis in patients after acute coronary syndromes (ACS) is significantly burdened by coexisting anaemia, leukocytosis and low glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Hyperglycaemia in the early stages of ACS is a strong predictor of death and heart failure in non-diabetic subjects. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of hyperglycaemia, anaemia, leukocytosis, thrombocytopaenia and decreased GFR on the risk of the failure of cardiac rehabilitation (phase II at the hospital) in post-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients.
Methods: The study included 136 post-STEMI patients, 96 men and 40 women, aged 60.1 ± 11.8 years, admitted for cardiac rehabilitation (phase II) to the Department of Internal Medicine and Cardiac Rehabilitation, WAM University Hospital in Lodz, Poland. On admission fasting blood cell count was performed and serum glucose and creatinine level was determined (GFR assessment). The following results were considered abnormal: glucose ⩾ 100 mg/dl, GFR < 60 ml/min/1, 73 m², red blood cells (RBCs) < 4 × 106/μl, white blood cells (WBCs) > 10 × 103/μl; platelets (PLTs) < 150 × 10³/ml. In all patients an exercise test was performed twice, before and after the completion of the second stage of rehabilitation, to assess its effects.
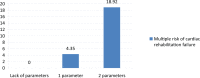
Results: Based on logistic regression analysis and the results of an individual odds ratio (OR) of the tested parameters, their prognostic impact was determined on the risk of failure of cardiac rehabilitation. This risk has been defined on the basis of the patient's inability to tolerate workload increment >5 Watt in spite of the applied program of cardiac rehabilitation. As a result of building a logistic regression model, the most statistically significant risk factors were selected, on the basis of which cardiac rehabilitation failure index was determined. leukocytosis and reduced GFR determined most significantly the risk of failure of cardiac rehabilitation (respectively OR = 6.42 and OR = 3.29, p = 0.007). These parameters were subsequently utilized to construct a rehabilitation failure index.
Conclusions: Peripheral blood cell count and GFR are important in assessing the prognosis of cardiac rehabilitation effects. leukocytosis and decreased GFR determine to the highest degree the risk of cardiac rehabilitation failure. Cardiac rehabilitation failure index may be useful in classifying patients into an appropriate model of rehabilitation. These findings support our earlier reports.
Keywords: acute coronary syndrome; cardiac rehabilitation; glomerular filtration rate; leucocytosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Stone GW, Machara A, Lansky AJ. A prospective natural-history study of coronary atherosclerosis. N Engl J Med 2011; 364: 226–235. - PubMed
-
- Meune C, Drexler B, Haaf P. The GRACE score’s performance in predicting in-hospital and 1-year outcome in the era of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin assays and B-type natriuretic peptide. Heart 2011; 97: 1479–1483. - PubMed
-
- Terlecki M, Bednarek A, Kawecka-Jaszcz K, et al. Acute hyperglycaemia and inflammation in patients with ST segment elevation myocardial infarction. Kardiol Pol 2013; 71: 260–267. - PubMed
-
- Al Suwaidi J, Reddan DN, Williams K, et al. Prognostic implications of abnormalities in renal function in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Circulation 2002; 106: 974–980. - PubMed
-
- Wang TY, Ou FS, Roe MT, et al. Incidence and prognostic significance of thrombocytopenia developed during acute coronary syndrome in contemporary clinical practice. Circulation 2009; 119: 2454–2462. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials