The Expanding Significance of Inositol Polyphosphate Multikinase as a Signaling Hub
- PMID: 28554203
- PMCID: PMC5463039
- DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2017.0066
The Expanding Significance of Inositol Polyphosphate Multikinase as a Signaling Hub
Abstract
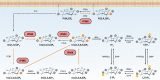
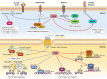
The inositol polyphosphates are a group of multifunctional signaling metabolites whose synthesis is catalyzed by a family of inositol kinases that are evolutionarily conserved from yeast to humans. Inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) was first identified as a subunit of the arginine-responsive transcription complex in budding yeast. In addition to its role in the production of inositol tetrakis- and pentakisphosphates (IP4 and IP5), IPMK also exhibits phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-kinase) activity. Through its PI3-kinase activity, IPMK activates Akt/PKB and its downstream signaling pathways. IPMK also regulates several protein targets non-catalytically via protein-protein interactions. These non-catalytic targets include cytosolic signaling factors and transcription factors in the nucleus. In this review, we highlight the many known functions of mammalian IPMK in controlling cellular signaling networks and discuss future challenges related to clarifying the unknown roles IPMK plays in physiology and disease.
Keywords: IPMK; PI3-kinase; inositol; inositol phosphates; inositol polyphosphate multikinase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inositol polyphosphate multikinase signaling in the regulation of metabolism.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012 Oct;1271(1):68-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06725.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012. PMID: 23050966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inositol polyphosphate multikinase is a physiologic PI3-kinase that activates Akt/PKB.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jan 25;108(4):1391-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1017831108. Epub 2011 Jan 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21220345 Free PMC article.
-
IPMK: A versatile regulator of nuclear signaling events.Adv Biol Regul. 2016 May;61:25-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2015.11.005. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Adv Biol Regul. 2016. PMID: 26682649 Review.
-
Inositol Polyphosphate Multikinase Signaling: Multifaceted Functions in Health and Disease.Mol Cells. 2021 Apr 30;44(4):187-194. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2021.0045. Mol Cells. 2021. PMID: 33935040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inositol Polyphosphate Multikinase Inhibits Angiogenesis via Inositol Pentakisphosphate-Induced HIF-1α Degradation.Circ Res. 2018 Feb 2;122(3):457-472. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311983. Epub 2017 Dec 26. Circ Res. 2018. PMID: 29279301 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Inositol phosphates promote HIV-1 assembly and maturation to facilitate viral spread in human CD4+ T cells.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Jan 21;17(1):e1009190. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009190. eCollection 2021 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33476323 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Skeletal Muscle Inositol Polyphosphate Multikinase Disrupts Glucose Regulation and Limits Exercise Capacity.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 7;26(6):2395. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062395. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141045 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol polyphosphate multikinase mediates extinction of fear memory.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Feb 12;116(7):2707-2712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1812771116. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30692248 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear lipid mediators: Role of nuclear sphingolipids and sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling in epigenetic regulation of inflammation and gene expression.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Aug;119(8):6337-6353. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26707. Epub 2018 May 8. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29377310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide interaction studies identify sex-specific risk alleles for nonsyndromic orofacial clefts.Genet Epidemiol. 2018 Oct;42(7):664-672. doi: 10.1002/gepi.22158. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Genet Epidemiol. 2018. PMID: 30277614 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

