Role of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide and N-Terminal Prohormone BNP as Predictors of Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality in Patients With a Recent Coronary Event and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 28554908
- PMCID: PMC5669146
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004743
Role of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide and N-Terminal Prohormone BNP as Predictors of Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality in Patients With a Recent Coronary Event and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
Background: Natriuretic peptides are recognized as important predictors of cardiovascular events in patients with heart failure, but less is known about their prognostic importance in patients with acute coronary syndrome. We sought to determine whether B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal prohormone B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) could enhance risk prediction of a broad range of cardiovascular outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
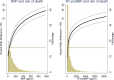
Methods and results: Patients with a recent acute coronary syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus were prospectively enrolled in the ELIXA trial (n=5525, follow-up time 26 months). Best risk models were constructed from relevant baseline variables with and without BNP/NT-proBNP. C statistics, Net Reclassification Index, and Integrated Discrimination Index were analyzed to estimate the value of adding BNP or NT-proBNP to best risk models. Overall, BNP and NT-proBNP were the most important predictors of all outcomes examined, irrespective of history of heart failure or any prior cardiovascular disease. BNP significantly improved C statistics when added to risk models for each outcome examined, the strongest increments being in death (0.77-0.82, P<0.001), cardiovascular death (0.77-0.83, P<0.001), and heart failure (0.84-0.87, P<0.001). BNP or NT-proBNP alone predicted death as well as all other variables combined (0.77 versus 0.77).
Conclusions: In patients with a recent acute coronary syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus, BNP and NT-proBNP were powerful predictors of cardiovascular outcomes beyond heart failure and death, ie, were also predictive of MI and stroke. Natriuretic peptides added as much predictive information about death as all other conventional variables combined.
Clinical trial registration: URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT01147250.
Keywords: Evaluation of Lixisenatide in Acute Coronary Syndrome trial; N‐terminal prohormone B‐type natriuretic peptide; acute coronary syndrome; biomarker; brain natriuretic peptide; cardiac outcomes; diabetes mellitus; glucagon‐like peptide‐1; natriuretic peptide; risk model.
© 2017 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical and Biomarker Predictors of Expanded Heart Failure Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus After a Recent Acute Coronary Syndrome: Insights From the EXAMINE Trial.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Jan 7;9(1):e012797. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012797. Epub 2020 Jan 4. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 31902327 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
B-type natriuretic peptides for the prediction of cardiovascular events in patients with stable coronary heart disease: the Heart and Soul Study.J Am Heart Assoc. 2014 Jul 22;3(4):e000907. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.114.000907. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014. PMID: 25053234 Free PMC article.
-
Usefulness of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic Peptide levels for stroke risk prediction in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation.Stroke. 2014 Mar;45(3):696-701. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.003338. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Stroke. 2014. PMID: 24519407
-
B-type natriuretic peptides: prognostic markers in stable coronary artery disease.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2008 Mar;8(2):217-25. doi: 10.1586/14737159.8.2.217. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2008. PMID: 18366308 Review.
-
Clinical implications of B-type natriuretic peptide and N-terminal pro--B-type natriuretic peptide in the care of the vascular surgery patient.Semin Vasc Surg. 2014 Dec;27(3-4):143-7. doi: 10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2015.01.004. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Semin Vasc Surg. 2014. PMID: 26073822 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of body mass index on N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide values in patients with heart failure.Egypt Heart J. 2023 Aug 29;75(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s43044-023-00401-1. Egypt Heart J. 2023. PMID: 37642755 Free PMC article.
-
From Classic to Modern Prognostic Biomarkers in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 15;23(16):9168. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169168. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood pressure and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and a recent coronary event in the ELIXA trial.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Oct 12;19(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01150-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 33046070 Free PMC article.
-
NT-proBNP as a predictor of death and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2022 May 3;14(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s13098-022-00837-6. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2022. PMID: 35501909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardioprotective and Antifibrotic Effects of Low-Dose Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors in Type 1 Diabetic Rat Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 1;24(23):17043. doi: 10.3390/ijms242317043. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haffner SM, Lehto S, Rönnemaa T, Pyörälä K, Laakso M. Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:229–234. - PubMed
-
- Beckman JA, Creager MA, Libby P. Diabetes and atherosclerosis: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. JAMA. 2002;287:2570–2581. - PubMed
-
- Scirica BM, Kadakia MB, de Lemos JA, Roe MT, Morrow DA, Li S, Wiviott SD, Kontos MC. Association between natriuretic peptides and mortality among patients admitted with myocardial infarction: a report from the ACTION Registry®–GWTGTM . Clin Chem. 2013;59:1205–1214. - PubMed
-
- Jhund PS, Anand IS, Komajda M, Claggett BL, McKelvie RS, Zile MR, Carson PE, McMurray JJV. Changes in N‐terminal pro‐B‐type natriuretic peptide levels and outcomes in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: an analysis of the I‐Preserve study. Eur J Heart Fail. 2015;17:809–817. - PubMed
-
- Kristensen SL, Jhund PS, Køber L, McKelvie RS, Zile MR, Anand IS, Komajda M, Cleland JGF, Carson PE, McMurray JJV. Relative importance of history of heart failure hospitalization and N‐terminal pro‐B‐type natriuretic peptide level as predictors of outcomes in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction. JACC Heart Fail. 2015;3:478–486. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

