Collagen from the Marine Sponges Axinella cannabina and Suberites carnosus: Isolation and Morphological, Biochemical, and Biophysical Characterization
- PMID: 28555046
- PMCID: PMC5484102
- DOI: 10.3390/md15060152
Collagen from the Marine Sponges Axinella cannabina and Suberites carnosus: Isolation and Morphological, Biochemical, and Biophysical Characterization
Abstract
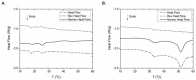
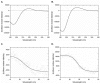
In search of alternative and safer sources of collagen for biomedical applications, the marine demosponges Axinella cannabina and Suberites carnosus, collected from the Aegean and the Ionian Seas, respectively, were comparatively studied for their insoluble collagen, intercellular collagen, and spongin-like collagen content. The isolated collagenous materials were morphologically, physicochemically, and biophysically characterized. Using scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy the fibrous morphology of the isolated collagens was confirmed, whereas the amino acid analysis, in conjunction with infrared spectroscopy studies, verified the characteristic for the collagen amino acid profile and its secondary structure. Furthermore, the isoelectric point and thermal behavior were determined by titration and differential scanning calorimetry, in combination with circular dichroism spectroscopic studies, respectively.
Keywords: Axinella cannabina; Suberites carnosus; marine collagen; sponges.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Meena C., Mengi S.A., Deshpande S.G. Biomedical and industrial applications of collagen. J. Chem. Sci. 1999;111:319–329. doi: 10.1007/BF02871912. - DOI
-
- Berillis P. Marine collagen: Extraction and applications. In: Madhukar S., editor. Research Trends in Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Microbiology. SM Group; Dover, DE, USA: 2015. pp. 1–13.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

