HIF-1α is required for disturbed flow-induced metabolic reprogramming in human and porcine vascular endothelium
- PMID: 28556776
- PMCID: PMC5495571
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.25217
HIF-1α is required for disturbed flow-induced metabolic reprogramming in human and porcine vascular endothelium
Abstract
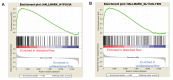
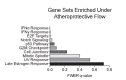
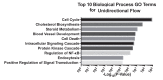
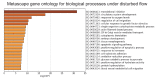
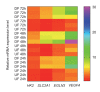
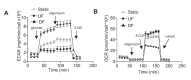
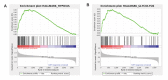
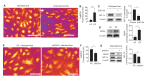
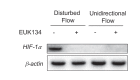
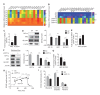
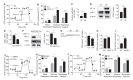
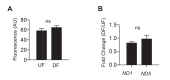
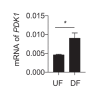
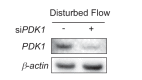
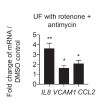
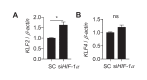
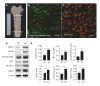
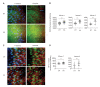
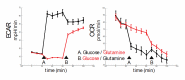
Hemodynamic forces regulate vascular functions. Disturbed flow (DF) occurs in arterial bifurcations and curvatures, activates endothelial cells (ECs), and results in vascular inflammation and ultimately atherosclerosis. However, how DF alters EC metabolism, and whether resulting metabolic changes induce EC activation, is unknown. Using transcriptomics and bioenergetic analysis, we discovered that DF induces glycolysis and reduces mitochondrial respiratory capacity in human aortic ECs. DF-induced metabolic reprogramming required hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), downstream of NAD(P)H oxidase-4 (NOX4)-derived reactive oxygen species (ROS). HIF-1α increased glycolytic enzymes and pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase-1 (PDK-1), which reduces mitochondrial respiratory capacity. Swine aortic arch endothelia exhibited elevated ROS, NOX4, HIF-1α, and glycolytic enzyme and PDK1 expression, suggesting that DF leads to metabolic reprogramming in vivo. Inhibition of glycolysis reduced inflammation suggesting a causal relationship between flow-induced metabolic changes and EC activation. These findings highlight a previously uncharacterized role for flow-induced metabolic reprogramming and inflammation in ECs.
Keywords: Porcine; cell biology; hemodynamics; human; mechanotransduction; metabolism; mouse.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures








References
-
- Akhtar S, Hartmann P, Karshovska E, Rinderknecht FA, Subramanian P, Gremse F, Grommes J, Jacobs M, Kiessling F, Weber C, Steffens S, Schober A. Endothelial Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α promotes Atherosclerosis and monocyte recruitment by upregulating MicroRNA-19a. Hypertension. 2015;66:1220–1226. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.05886. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bonello S, Zähringer C, BelAiba RS, Djordjevic T, Hess J, Michiels C, Kietzmann T, Görlach A. Reactive oxygen species activate the HIF-1alpha promoter via a functional NFkappaB site. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2007;27:755–761. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000258979.92828.bc. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

