Farnesyltransferase inhibitor FTI-277 inhibits PD-L1 expression on septic spleen lymphocytes and promotes spleen lymphocyte activation
- PMID: 28556912
- PMCID: PMC5588849
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.12995
Farnesyltransferase inhibitor FTI-277 inhibits PD-L1 expression on septic spleen lymphocytes and promotes spleen lymphocyte activation
Abstract
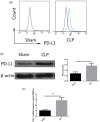
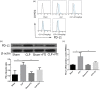
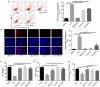
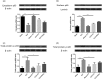
Farnesyltransferase inhibitors have been tested in clinical trials for the treatment of tumours. In sepsis, the binding of programmed death 1 (PD-1) to programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) promotes lymphocyte apoptosis and decreases cytokine expression, thus affecting survival rates. The PD-1/PD-L1 pathway plays an important role in chronic viral infection, bacterial infection and sepsis. However, the precise immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory functions of this pathway remain poorly understood. In our previous study, the induction of sepsis by caecal ligation and puncture (CLP) resulted in increased farnesyltransferase activity and farnesylated protein levels in the spleen relative to sham treatment. However, the effect of inhibition of farnesyltransferase activity on overall survival rates in patients with sepsis and the specific signalling pathway involved remain to be investigated. In this study, mice with CLP-induced sepsis were treated with farnesyltransferase inhibitor (FTI-277), and PD-L1 expression on septic spleen lymphocytes was examined. Flow cytometric analysis revealed that PD-L1 is expressed constitutively on lymphocytes and that PD-L1 protein expression was up-regulated strongly following CLP. FTI-277 down-regulated PD-L1 mRNA and protein expression on septic spleen lymphocytes in a dose-dependent manner. This effect was associated closely with nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB). In addition, the significant damping effect of FTI-277 on the PD-L1 signal promoted interferon (IFN)-γ secretion, interleukin (IL)-2 production and splenocyte proliferation in response to anti-CD3+ CD28+ antibodies in mice. Furthermore, FTI-277 reduced spleen lymphocyte apoptosis in septic mice. Therefore, FTI-277 regulates spleen lymphocyte activity via the PD-L1 signalling pathway, with significant anti-inflammatory effects attributable to suppression of the NF-κB pathway. Farnesyltransferase represents a valuable therapeutic target for the treatment of sepsis.
Keywords: T cells; inflammation; molecular biology; transcription factors.
© 2017 British Society for Immunology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Farnesyltransferase inhibitor FTI-277 reduces mortality of septic mice along with improved bacterial clearance.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Dec;339(3):832-41. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.183558. Epub 2011 Aug 26. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21873557 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamine Administration in Early or Late Septic Phase Downregulates Lymphocyte PD-1/PD-L1 Expression and the Inflammatory Response in Mice With Polymicrobial Sepsis.JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2018 Mar;42(3):538-549. doi: 10.1177/0148607117695245. Epub 2017 Dec 12. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2018. PMID: 28633555
-
[Effects and molecular mechanism of histone methyltransferase enhancer of zeste homolog 2 on regulating sepsis-induced T cell dysfunction].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022 Apr;34(4):357-361. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20210906-01323. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022. PMID: 35692198 Chinese.
-
Regulation of PD-L1: a novel role of pro-survival signalling in cancer.Ann Oncol. 2016 Mar;27(3):409-16. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv615. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Ann Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26681673 Review.
-
The PD-1/PD-L1 (B7-H1) pathway in chronic infection-induced cytotoxic T lymphocyte exhaustion.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:451694. doi: 10.1155/2011/451694. Epub 2011 Sep 25. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21960736 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
What role does PDL1 play in EMT changes in tumors and fibrosis?Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 15;14:1226038. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1226038. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37649487 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dombrovskiy VY, Martin AA, Sunderram J, Paz HL. Rapid increase in hospitalization and mortality rates for severe sepsis in the United States: a trend analysis from 1993 to 2003. Crit Care Med 2007; 35:1244–50. - PubMed
-
- Brown JA, Dorfman DM, Ma FR et al Blockade of programmed death‐1 ligands on dendritic cells enhances T cell activation and cytokine production. J Immunol 2003; 170:1257–66. - PubMed
-
- Saresella M, Rainone V, Al‐Daghri NM, Clerici M, Trabattoni D. The PD‐1/PD‐L1 pathway in human pathology. Curr Mol Med 2012; 12:259–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

