Race and Obesity in Adolescent Hypertension
- PMID: 28557717
- PMCID: PMC5404724
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2016-1433
Race and Obesity in Adolescent Hypertension
Abstract
Background and objectives: The overall prevalence of essential hypertension in adolescents may be growing. Differences in blood pressure (BP) are well established in adults, but are less clear in adolescents. We hypothesize that the prevalence of hypertension differs by race/ethnicity among adolescents at school-based screenings.
Methods: We performed school-based BP screening in over 20 000 adolescents from 2000 to 2015. Race/ethnicity was self-reported. Height and weight were measured to determine BMI, and BP status was confirmed on 3 occasions to diagnose sustained hypertension according to Fourth Working Group Report criteria.
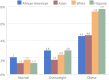
Results: We successfully screened 21 062 adolescents aged 10 to 19 years (mean, 13.8 years). The final prevalence of sustained hypertension in all subjects was 2.7%. Obesity rates were highest among African American (3.1%) and Hispanic (2.7%) adolescents. The highest rate of hypertension was seen in Hispanic (3.1%), followed by African American (2.7%), white (2.6%), and Asian (1.7%) adolescents (P = .019). However, obese white adolescents had the highest prevalence of sustained hypertension (7.4%) compared with obese African American adolescents (4.5%, P < .001). At lower BMI percentiles (<60th percentile), Hispanic adolescents actually had the lowest predicted prevalence of hypertension among the 4 groups.
Conclusions: The prevalence of hypertension varies among different race/ethnicities. Although obesity remains the strongest predictor of early hypertension, the strength of this relationship is intensified in Hispanic and white adolescents, whereas it is lessened in African American adolescents.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Conflict of interest statement
POTENTIAL CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors have indicated they have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Ogden CL, Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Johnson CL. Prevalence and trends in overweight among US children and adolescents, 1999-2000. JAMA. 2002;288(14):1728–1732 - PubMed
-
- Skinner AC, Skelton JA. Prevalence and trends in obesity and severe obesity among children in the United States, 1999-2012. JAMA Pediatr. 2014;168(6):561–566 - PubMed
-
- Din-Dzietham R, Liu Y, Bielo MV, Shamsa F. High blood pressure trends in children and adolescents in national surveys, 1963 to 2002. Circulation. 2007;116(13):1488–1496 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

