Reverse epitope mapping of the E2 glycoprotein in antibody associated hepatitis C virus
- PMID: 28558001
- PMCID: PMC5448734
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175349
Reverse epitope mapping of the E2 glycoprotein in antibody associated hepatitis C virus
Abstract
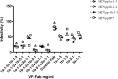
The humoral immune system responds to chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection by producing neutralising antibodies (nAb). In this study we generated three HCV pseudoparticles in which E1E2 glycoprotein sequence was targeted by the host humoral immune system. We used patient derived virus free Fabs (VF-Fabs) obtained from HCV genotype 1a (n = 3), genotype 1b (n = 7) and genotype 3a (n = 1) for neutralisation of HCVpp produced in this study both individually and in combination. Based on the available anti-HCV monoclonal nAb mapping information we selected amino acid region 384-619 for conformational epitope mapping. Amongst our notable findings, we observed significant reduction in HCVpp infectivity (p<0.05) when challenged with a combination of inter genotype and subtype VF-Fabs. We also identified five binding motifs targeted by patient derived VF-Fab upon peptide mapping, of which two shared the residues with previously reported epitopes. One epitope lies within an immunodominant HVR1 and two were novel. In summary, we used a reverse epitope mapping strategy to identify preferred epitopes by the host humoral immune system. Additionally, we have combined different VF-Fabs to further reduce the HCVpp infectivity. Our data indicates that combining the antigen specificity of antibodies may be a useful strategy to reduce (in-vitro) infectivity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Humoral immune system targets clonotypic antibody-associated hepatitis C virus.J Gen Virol. 2017 Feb;98(2):179-189. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000659. J Gen Virol. 2017. PMID: 28284234
-
Fine mapping of murine antibody responses to immunization with a novel soluble form of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein complex.J Virol. 2014 Sep;88(18):10459-71. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01584-14. Epub 2014 Jun 25. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24965471 Free PMC article.
-
Human monoclonal antibodies to a novel cluster of conformational epitopes on HCV E2 with resistance to neutralization escape in a genotype 2a isolate.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(4):e1002653. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002653. Epub 2012 Apr 12. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22511875 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Hypervariable Region 1 in Envelope Protein 2 of Hepatitis C Virus: A Linchpin in Neutralizing Antibody Evasion and Viral Entry.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 27;9:2146. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02146. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30319614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural perspectives on HCV humoral immune evasion mechanisms.Curr Opin Virol. 2021 Aug;49:92-101. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2021.05.002. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Curr Opin Virol. 2021. PMID: 34091143 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epitope Mapping of Exposed Tegument and Alimentary Tract Proteins Identifies Putative Antigenic Targets of the Attenuated Schistosome Vaccine.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 3;11:624613. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.624613. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33763055 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the epitopes of Schistosoma japonicum esophageal gland proteins for incorporation into vaccine constructs.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 27;15(2):e0229542. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229542. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32107503 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary modeling reveals enhanced mutational flexibility of HCV subtype 1b compared with 1a.iScience. 2021 Dec 8;25(1):103569. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103569. eCollection 2022 Jan 21. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34988406 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bowen DG, Walker CM. Adaptive immune responses in acute and chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Nature. 2005;436(7053):946–52. doi: 10.1038/nature04079 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sabo MC, Luca VC, Prentoe J, Hopcraft SE, Blight KJ, Yi M, et al. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against hepatitis C virus E2 protein bind discontinuous epitopes and inhibit infection at a postattachment step. Journal of virology. 2011;85(14):7005–19. PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3126585. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00586-11 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Keck ZY, Li SH, Xia J, von Hahn T, Balfe P, McKeating JA, et al. Mutations in hepatitis C virus E2 located outside the CD81 binding sites lead to escape from broadly neutralizing antibodies but compromise virus infectivity. Journal of virology. 2009;83(12):6149–60. PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC2687388. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00248-09 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Keck ZY, Xia J, Wang Y, Wang W, Krey T, Prentoe J, et al. Human monoclonal antibodies to a novel cluster of conformational epitopes on HCV E2 with resistance to neutralization escape in a genotype 2a isolate. PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(4):e1002653 PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3325216. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002653 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

