Modern peptide biomarkers and echocardiography in cardiac healthy haemodialysis patients
- PMID: 28558715
- PMCID: PMC5450351
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-017-0589-3
Modern peptide biomarkers and echocardiography in cardiac healthy haemodialysis patients
Abstract
Background: In this prospective study, we aimed to assess the haemodynamic changes before and after haemodialysis (HD) in cardiac healthy subjects on chronic HD by imaging methods and endocrine markers of fluid balance.
Methods: Mid-regional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide (MR-proANP), N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), vasopressin (AVP) and copeptin (CT-proAVP), metanephrines and normetanephrines, renin and aldosterone, standard transthoracic echocardiography and diameter of vena cava inferior (VCID) were performed in 20 patients with end stage renal disease (CKD5D) before and after HD and were stratified in residual excretion (RE, less or more 0.5 l) and ultrafiltration rate (UF, less or more 2 l).
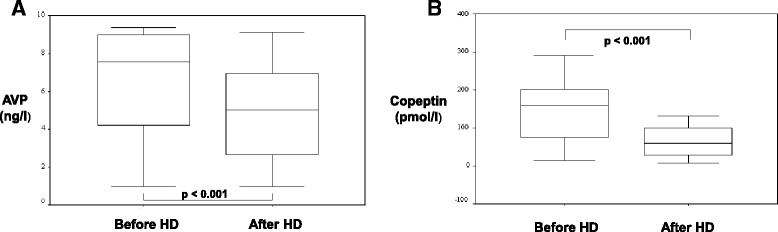
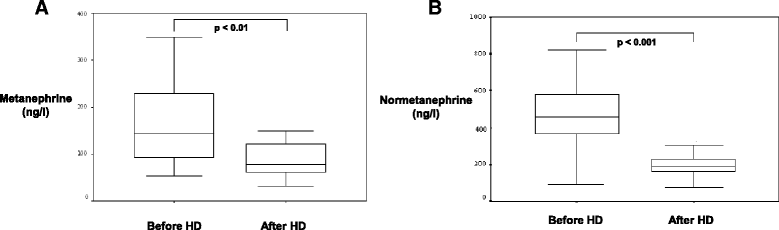
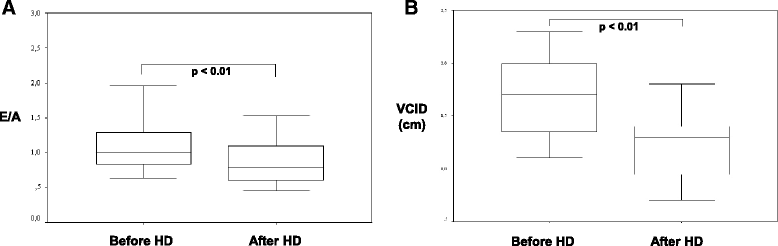
Results: Copeptin was significantly higher in patients before HD. Copeptin was inversely correlated with haemodialysis treatment adequacy (KT/v), RE and UF, but was not significantly influenced by age, gender and body mass index (BMI). MR-proANP was significantly reduced by haemodialysis by 27% and was inversely correlated with KT/v, but there was a significant influence by UF, RE, age, gender and BMI. NT-proBNP was significantly higher in patients before HD and was not influenced by RE and UF. Renin, aldosterone, metanephrines and normetanephrines did not demonstrate significant differences. Echocardiographic parameters and VCID were significantly correlated with RE, UF and copeptin.
Conclusion: Modern biomarkers will provide cardiovascular risk assessment, but elimination (UF), RE and other factors may influence the serum concentrations, e.g. in patients with renal impairment. The interpretation will be limited by altered reference ranges, and will be restricted to individual courses combined with clinical and echocardiographic data.
Keywords: AVP; Cardiorenal syndrome; Copeptin; Haemodialysis; Left ventricular dysfunction; MR-proANP; NT-proBNP.
Figures

Similar articles
-
N-Terminal Prohormone of Brain Natriuretic Peptide but not C-Terminal Pre-Pro Vasopressin (Copeptin) Level is Associated with the Response to Antihypertensive Therapy in Haemodialysis Patients.Kidney Blood Press Res. 2017;42(6):1013-1022. doi: 10.1159/000485433. Epub 2017 Nov 30. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2017. PMID: 29190613
-
Prognostic performance of serial in-hospital measurements of copeptin and multiple novel biomarkers among patients with worsening heart failure: results from the MOLITOR study.ESC Heart Fail. 2018 Apr;5(2):288-296. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12231. Epub 2018 Feb 24. ESC Heart Fail. 2018. PMID: 29476612 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Short-Term Influence of Radiofrequency Ablation on NT-proBNP, MR-proANP, Copeptin, and MR-proADM in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Data From the Observational SMURF Study.J Am Heart Assoc. 2016 Sep 15;5(9):e003557. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003557. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016. PMID: 27633393 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular biomarkers in patients with cancer and their association with all-cause mortality.Heart. 2015 Dec;101(23):1874-80. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2015-307848. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Heart. 2015. PMID: 26416836
-
Diagnostic utility of MR-proANP and NT-proBNP in elderly outpatients with a high risk of heart failure: the Copenhagen heart failure risk study.Biomarkers. 2020 May;25(3):248-259. doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2020.1732466. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Biomarkers. 2020. PMID: 32126847
Cited by
-
Dialysate copeptin and peritoneal transport in incident peritoneal dialysis patients.Int Urol Nephrol. 2019 Sep;51(9):1667-1673. doi: 10.1007/s11255-019-02191-5. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Int Urol Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31187425 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

