Assessment of physical activity, capacity and nutritional status in elderly peritoneal dialysis patients
- PMID: 28558794
- PMCID: PMC5450102
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-017-0593-7
Assessment of physical activity, capacity and nutritional status in elderly peritoneal dialysis patients
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to evaluate the prevalence of sedentarism, and to assess physical capacity and nutritional status in a cohort of older patients on peritoneal dialysis (PD), with respect to age-matched non-dialysis CKD population, using highly accessible, simple methods, namely the Rapid Assessment of Physical activity (RAPA) test and the 30″ Sit-to-stand (STS) test.
Methods: This cross-sectional multicenter study included 151 renal patients older than 60 years; 71 pts. (44 m, age 72 ± 7 yrs) were on PD and 80 pts. (63 m, age 74 ± 7 yrs) were affected by 3-4 stage CKD.
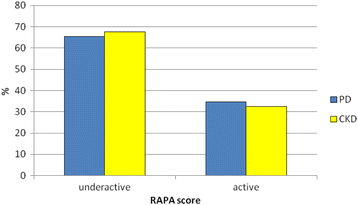
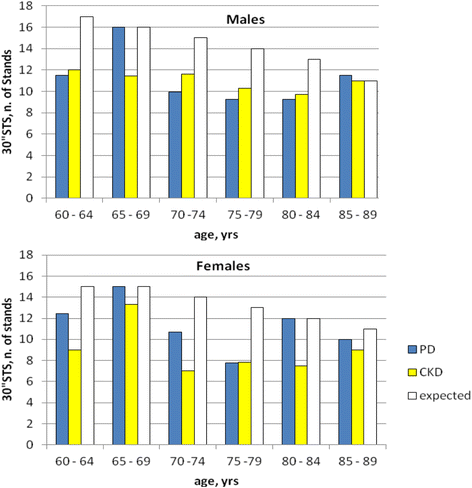
Results: The prevalence of sedentary/underactive patients was double of that of the active patients as assessed by RAPA test, both in the PD (65.3%) and in the CKD (67.5%) cohort. The 30"STS test showed a reduced physical performance in both groups: 84.5% of PD patients and 87.5% of CKD patients did not reach the expected number of stands by age and gender. A malnutrition-inflammation score (MIS) ≥ 6 occurred in 37 % of PD patients and in 2.5 % of CKD patients. In PD patients, an independent significant association was observed between 30"STS test and MIS (beta -0.510, p = 0.013), as well as between RAPA and MIS (beta -0.544, p = 003) and phase angle (beta -0.506, p = 0.028).
Conclusions: A high prevalence of low- performance capacity and sedentarism has been detected among elderly patients on PD or with CKD stage 3-4. Apart from age, a condition of malnutrition-inflammation was the major determinant of poor physical activity and capacity in PD patients. Better body composition seems to be positively associated with physical activity in PD and with physical capacity in CKD patients. Routine clinical management should include a close evaluation of nutritional status and evaluation of physical activity and capacity which can be easily assessed by RAPA and 30″STS tests.
Keywords: CKD; Esrd; MIS; Nutritional status; Performance; Peritoneal dialysis; Physical activity; Rapa.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

