In vitro quality evaluation of leading brands of ciprofloxacin tablets available in Bangladesh
- PMID: 28558832
- PMCID: PMC5450125
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-017-2507-y
In vitro quality evaluation of leading brands of ciprofloxacin tablets available in Bangladesh
Abstract
Background: Ciprofloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that acts against a number of bacterial infections. The study was carried out to examine the in vitro quality control tests for ten leading brands of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride 500 mg tablet formulation, registered in Bangladesh by Directorate General of Drug Administration. The quality control parameters of ten different brands of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride 500 mg tablets were determined by weight variation, friability, hardness, disintegration, dissolution and assay tests. All the tablets were evaluated for conformity with United States Pharmacopoeia-National Formulary (USP-NF) and British Pharmacopoeia (BP) standards.
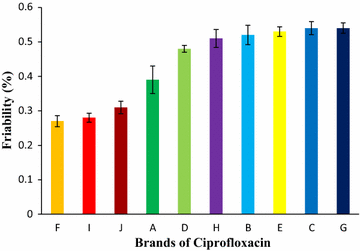
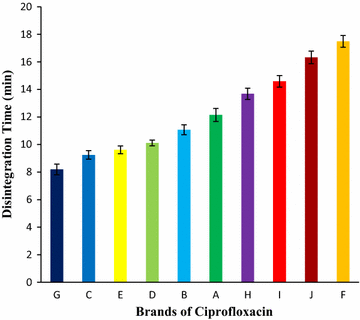
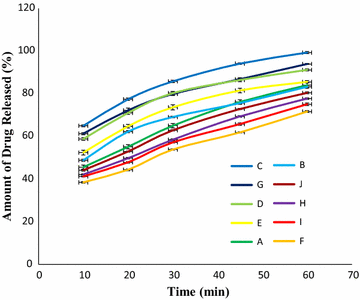
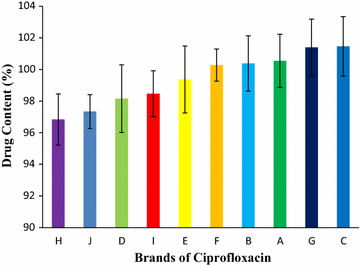
Results: Among ten brands of tablets Brand C had lower mean weight variation of 1.59% and Brand E had highest mean weight variation of 3.32%. For friability test Brand F had lowest mean friability (0.27%) and Brand G had highest mean friability (0.54%). Among ten brands mean lowest and highest hardness were founded in Brand G (4.49 kg/cm2) and Brand F (7.13 kg/cm2) respectively. The disintegration time for ten brands of ciprofloxacin tablet obtained were in the subsequent order: Brand G (8.19 min) < Brand C (9.25 min) < Brand E (9.61 min) < Brand D (10.11 min) < Brand B (11.07 min) < Brand A (12.15 min) < Brand H (13.68 min) < Brand I (14.59 min) < Brand J (16.32 min) < Brand F (17.49 min). Among ten brands for dissolution test mean percentages of drug release were not less than 80% in 45 min for four tablets (Brand E, 81.52%; Brand D, 86.44%; Brand G, 86.82% and Brand C, 94.12%), consequently they met BP standard and as per USP-NF standard six brands (Brand B, 75.62%; Brand A, 76.18%; Brand E, 81.52%; Brand D, 86.44%; Brand G, 86.82% and Brand C, 94.12%) had released not less than 75% drugs, so they also complied with the standard. The percentages of the drug content of the ten brands of ciprofloxacin tablet were obtained in the following sequence: Brand H (96.84%) < Brand J (97.34%) < Brand D (98.15%) < Brand I (98.47%) < Brand E (99.37%) < Brand F (100.28%) < Brand B (100.38%) < Brand A (100.54%) < Brand G (101.39%) < Brand C (101.46%). All of the brands met the BP and USP-NF specifications for assay. First-order, Higuchi and Korsmeyer-Peppas kinetics model fit for all of the mentioned ten brands.
Conclusion: The present study revealed that all of the leading brands of this tablet met the quality control parameters as per pharmacopoeial specifications except dissolution test for four brands (Brand J, Brand H, Brand I, and Brand F).
Keywords: Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride; Leading brands; Pharmacopoeial specifications; Quality control.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In vitro comparative quality evaluation of different brands of carbamazepine tablets commercially available in Dessie town, Northeast Ethiopia.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023 May 25;24(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s40360-023-00670-1. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37231520 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmaceutical equivalent studies of some commercially available brands of Loratadine hydrochloride tablets.Afr J Med Med Sci. 2015 Sep;44(3):269-76. Afr J Med Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 27280240
-
Comparative Quality Control Study of Different Brands of Diclofenac Sodium Tablet Available in Local and Government Pharmacies by In-Vitro Testing.Cureus. 2020 Nov 5;12(11):e11348. doi: 10.7759/cureus.11348. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33304683 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro comparative quality evaluation of different brands of esomeprazole tablets available in selected community pharmacies in Dhaka, Bangladesh.BMC Res Notes. 2018 Mar 20;11(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s13104-018-3285-x. BMC Res Notes. 2018. PMID: 29554952 Free PMC article.
-
Choosing a medication brand: Excipients, food intolerance and prescribing in older people.Maturitas. 2018 Jan;107:103-109. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2017.11.001. Epub 2017 Nov 1. Maturitas. 2018. PMID: 29169573 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of a Two-Phase Experiment Design and Optimization Method to Formulate Ciprofloxacin-Loaded Bovine Serum Albumin Nanoparticles with High-Entrapment Efficiency for Targeting Urinary Tract Infections.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025 May 2;26(5):122. doi: 10.1208/s12249-025-03115-6. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025. PMID: 40316780
-
In vitro comparative quality assessment of different brands of norfloxacin tablets available in Jimma, Southwest Ethiopia.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Apr 17;13:1241-1249. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S189524. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31118565 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmaceutical quality evaluation of marketed vildagliptin tablets in Bangladesh based on the United States Pharmacopeia specifications.Narra J. 2022 Aug;2(2):e84. doi: 10.52225/narra.v2i2.84. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Narra J. 2022. PMID: 38449703 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation and evaluation of taste-masked oral disintegrating tablet containing tolterodine-loaded montmorillonite.Res Pharm Sci. 2023 Aug 20;18(5):528-540. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.383708. eCollection 2023 Sep-Oct. Res Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 37842521 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro Comparative Quality Assessment of Different Brands of Furosemide Tablets Marketed in Northwest Ethiopia.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Nov 24;14:5119-5128. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S280203. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 33262573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hamam HAB. Comparative in vitro evaluation of generic ciprofloxacin hydrochloride tablets. World J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2014;3(12):388–390.
-
- Hailu GS, Gutema GB, Asefaw AA, Hussen DA, Hadera MG. Comparative assessment of the physicochemical and in vitro bioavailability equivalence of cotrimoxazole tablets marketed in Tigray, Ethiopia. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2011;2(12):3210–3218.
-
- Anonymous. 19th WHO model list of essential medicines. http://www.who.int/medicines/publications/essentialmedicines/EML2015_8-M.... Accessed 12 Oct 2015.
-
- Anonymous. Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride. http://www.drugs.com/monograph/ciprofloxacin-hydrochloride.html. Accessed 12 Oct 2015.
-
- Hamilton Richard J. Tarascon pharmacopoeia. 15. Burlington: Jones & Bartlett Publishers; 2014.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

