Viral and cellular mRNA-specific activators harness PABP and eIF4G to promote translation initiation downstream of cap binding
- PMID: 28559344
- PMCID: PMC5474791
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1610417114
Viral and cellular mRNA-specific activators harness PABP and eIF4G to promote translation initiation downstream of cap binding
Abstract
Regulation of mRNA translation is a major control point for gene expression and is critical for life. Of central importance is the complex between cap-bound eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E), eIF4G, and poly(A) tail-binding protein (PABP) that circularizes mRNAs, promoting translation and stability. This complex is often targeted to regulate overall translation rates, and also by mRNA-specific translational repressors. However, the mechanisms of mRNA-specific translational activation by RNA-binding proteins remain poorly understood. Here, we address this deficit, focusing on a herpes simplex virus-1 protein, ICP27. We reveal a direct interaction with PABP that is sufficient to promote PABP recruitment and necessary for ICP27-mediated activation. PABP binds several translation factors but is primarily considered to activate translation initiation as part of the PABP-eIF4G-eIF4E complex that stimulates the initial cap-binding step. Importantly, we find that ICP27-PABP forms a complex with, and requires the activity of, eIF4G. Surprisingly, ICP27-PABP-eIF4G complexes act independently of the effects of PABP-eIF4G on cap binding to promote small ribosomal subunit recruitment. Moreover, we find that a cellular mRNA-specific regulator, Deleted in Azoospermia-like (Dazl), also employs the PABP-eIF4G interaction in a similar manner. We propose a mechanism whereby diverse RNA-binding proteins directly recruit PABP, in a non-poly(A) tail-dependent manner, to stimulate the small subunit recruitment step. This strategy may be particularly relevant to biological conditions associated with hypoadenylated mRNAs (e.g., germ cells/neurons) and/or limiting cytoplasmic PABP (e.g., viral infection, cell stress). This mechanism adds significant insight into our knowledge of mRNA-specific translational activation and the function of the PABP-eIF4G complex in translation initiation.
Keywords: DAZL; ICP27; mRNA-binding protein; mRNA-specific translational regulation; poly(A)-binding protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



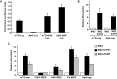

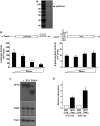
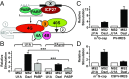
References
-
- Hentze MW, Gebauer F, Preiss T. cis-Acting regulatory sequences and trans-acting factors in translational control. In: Mathews MB, Sonenberg N, Hershey JWB, editors. Translational Control in Biology and Medicine. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor, NY: 2007. pp. 269–295.
-
- Michel YM, Poncet D, Piron M, Kean KM, Borman AM. Cap-Poly(A) synergy in mammalian cell-free extracts. Investigation of the requirements for poly(A)-mediated stimulation of translation initiation. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:32268–32276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

