Three New Lactobacillus plantarum Strains in the Probiotic Toolbox against Gut Pathogen Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhimurium
- PMID: 28559733
- PMCID: PMC5434365
- DOI: 10.17113/ftb.55.01.17.4693
Three New Lactobacillus plantarum Strains in the Probiotic Toolbox against Gut Pathogen Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhimurium
Abstract
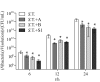
The benefits of probiotic bacteria have been widely explored. However, fermented foods and digestive system of humans and animals are an inexhaustible source of new potentially probiotic microorganisms. In this study we present three new Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from different dairy products: cow's cheese, sheep's cheese and whey. In order to determine the antibacterial activity of yet unexplored L. plantarum strains against Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium, in vitro competition and co-culture tests were done. Furthermore, adhesion of these strains to Caco-2 cells and their influence on the adhesion of Salmonella were tested. Results showed the potential probiotic activity of isolated strains. L. plantarum strains survived in the presence of 1% bile salts, they possessed acidification ability, antibacterial activity and significantly attenuated the growth of S. Typhimurium in brain heart infusion broth. All tested L. plantarum strains were able to adhere to Caco-2 cells and significantly impair the adhesion of S. Typhimurium. All three L. plantarum strains exhibited significant probiotic potential and anti-Salmonella activity; therefore, further testing on in vivo models should follow.
Keywords: Salmonella; antagonistic activity; mechanism of action; probiotic bacteria.
Figures


References
-
- Marteau PR, de Vrese M, Cellier CJ, Schrezenmeir J. Protection from gastrointestinal diseases with the use of probiotics. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001;73(2) Suppl:430S–6S. - PubMed
-
- Soccol CR, Vandenberghe LPDS, Spier MR, Medeiros ABP, Yamaguishi CT, De Dea Lindner J, et al. The potential of probiotics: a review. Food Technol Biotechnol. 2010;48:413–34.
-
- Health and nutritional properties of probiotics in food including powder milk with live lactic acid bacteria: Joint FAO/WHO Experts Consultation, October 2001. Geneva, Switzerland: Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations and World Health Organization (FAO/WHO): 2001. Available from: http://www.mesanders.com/probio_report.pdf.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
