MicroRNA-142-5p promotes cell growth and migration in renal cell carcinoma by targeting BTG3
- PMID: 28559989
- PMCID: PMC5446521
MicroRNA-142-5p promotes cell growth and migration in renal cell carcinoma by targeting BTG3
Abstract
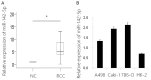
Purpose: Some microRNA (miRNA) levels have been found to be dysregulated in cancer patients, suggesting the potential usefulness of miRNAs in cancer therapies. The purpose of this study was to investigate the expression of miR-142-5p in human renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and its potential role in tumor growth and metastasis.
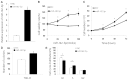
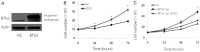
Methods: The expression level of miR-142-5p in human RCC tissue and cell lines was determined by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis. MTT, colony formation, Transwell, and cell cycle assays were performed to explore the potential functions of miR-142-5p in human RCC cells. The potential target gene of miR-142-5p was identified and confirmed via luciferase reporter assays.
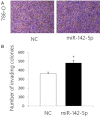
Results: miR-142-5p expression was elevated in RCC tissues and cell lines. Overexpression of miR-142-5p significantly promoted cell proliferation and colony formation and could prevent G1 phase arrest among RCC 786-O cells. Meanwhile, the migration potential of 786-O cells was greater than that of control cells. BTG3 was identified as a direct target of miR-142-5p, and re-expression of BTG3 reversed the miR-142-5p-induced cell proliferation.
Conclusion: miR-142-5p promoted the proliferation and migration of RCC cells by targeting BTG3. With this potential onco-miRNA role in the progression of RCC, miR-142-5p may be a therapeutic target for the treatment of RCC.
Keywords: BTG3; miR-142-5p; proliferation; renal cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Guo J, Ma J, Sun Y, Qin S, Ye D, Zhou F, He Z, Sheng X, Bi F, Cao D, Chen Y, Huang Y, Liang H, Liang J, Liu J, Liu W, Pan Y, Shu Y, Song X, Wang W, Wang X, Wu X, Xie X, Yao X, Yu S, Zhang Y, Zhou A. Chinese guidelines on the management of renal cell carcinoma (2015 edition) Ann Transl Med. 2015;3:279. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Bacik J, Mariani T, Russo P, Mazumdar M, Reuter V. Treatment outcome and survival associated with metastatic renal cell carcinoma of non-clear-cell histology. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002;20:2376–2381. - PubMed
-
- Lam JS, Shvarts O, Leppert JT, Figlin RA, Belldegrun AS. Renal cell carcinoma 2005: new frontiers in staging, prognostication and targeted molecular therapy. J Urol. 2005;173:1853–1862. - PubMed
-
- Capitanio U, Montorsi F. Renal cancer. Lancet. 2016;387:894–906. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
