Basics of Elbow Arthroscopy Part II: Positioning and Diagnostic Arthroscopy in the Supine Position
- PMID: 28560135
- PMCID: PMC5439242
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eats.2016.08.020
Basics of Elbow Arthroscopy Part II: Positioning and Diagnostic Arthroscopy in the Supine Position
Abstract
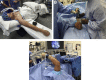
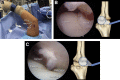
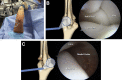
The field of elbow arthroscopy has evolved significantly since the procedure was first introduced more than 30 years ago. As our knowledge and understanding grows, numerous technical modifications have been made to improve the safety and efficacy of elbow arthroscopy. One of the most significant modifications is the change from the supine hanging position to the supine-suspended position with the use of a mechanical arm holder. Currently, the supine-suspended and lateral decubitus positions are the 2 most commonly used techniques. In this work, we discuss the history of the supine position, provide key points for proper patient positioning, and detail the steps of diagnostic elbow arthroscopy. It is our hope that this work will serve as an up-to-date review and summary of the most critical components of this procedure for emerging elbow arthroscopists.
Figures
References
-
- Andrews J.R., Carson W.G. Arthroscopy of the elbow. Arthroscopy. 1985;1:97–107. - PubMed
-
- Guhl J.F. Arthroscopy and arthroscopic surgery of the elbow. Orthopedics. 1985;8:1290–1296. - PubMed
-
- O'Driscoll S.W., Morrey B.F. Arthroscopy of the elbow. Diagnostic and therapeutic benefits and hazards. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74:84–94. - PubMed
-
- Field L.D., Altchek D.W., Warren R.F., O'Brien S.J., Skyhar M.J., Wickiewicz T.L. Arthroscopic anatomy of the lateral elbow: A comparison of three portals. Arthroscopy. 1994;10:602–607. - PubMed
-
- Adams J.E., King G.J., Steinmann S.P., Cohen M.S. Elbow arthroscopy: Indications, techniques, outcomes, and complications. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014;22:810–818. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

