Image reconstruction of oxidized cerebral cytochrome C oxidase changes from broadband near-infrared spectroscopy data
- PMID: 28560239
- PMCID: PMC5443419
- DOI: 10.1117/1.NPh.4.2.021105
Image reconstruction of oxidized cerebral cytochrome C oxidase changes from broadband near-infrared spectroscopy data
Abstract
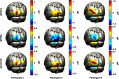
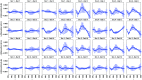
In diffuse optical tomography (DOT), overlapping and multidistance measurements are required to reconstruct depth-resolved images of oxy- ([Formula: see text]) and deoxy- (HHb) hemoglobin concentration changes occurring in the brain. These can be considered an indirect measure of brain activity, under the assumption of intact neurovascular coupling. Broadband systems also allow changes in the redox state of cytochrome c oxidase (oxCCO) to be measured, which can be an important biomarker when neurovascular coupling is impaired. We used DOT to reconstruct images of [Formula: see text], [Formula: see text], and [Formula: see text] from data acquired with a broadband system. Four healthy volunteers were measured while performing a visual stimulation task (4-Hz inverting checkerboard). The broadband system was configured to allow multidistance and overlapping measurements of the participants' visual cortex with 32 channels. A multispectral approach was employed to reconstruct changes in concentration of the three chromophores during the visual stimulation. A clear and focused activation was reconstructed in the left occipital cortex of all participants. The difference between the residuals of the three-chromophore model and of the two-chromophore model (recovering only [Formula: see text] and [Formula: see text]) exhibits a spectrum similar to that of oxCCO. These results form a basis for further studies aimed to further optimize image reconstruction of [Formula: see text].
Keywords: broadband; cytochrome C oxidase; functional near-infrared spectroscopy; image reconstruction; visual stimulation.
Figures





References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

