Toward real-time quantification of fluorescence molecular probes using target/background ratio for guiding biopsy and endoscopic therapy of esophageal neoplasia
- PMID: 28560244
- PMCID: PMC5443417
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JMI.4.2.024502
Toward real-time quantification of fluorescence molecular probes using target/background ratio for guiding biopsy and endoscopic therapy of esophageal neoplasia
Abstract
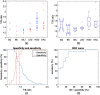
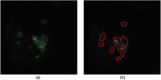
Multimodal endoscopy using fluorescence molecular probes is a promising method of surveying the entire esophagus to detect cancer progression. Using the fluorescence ratio of a target compared to a surrounding background, a quantitative value is diagnostic for progression from Barrett's esophagus to high-grade dysplasia (HGD) and esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC). However, current quantification of fluorescent images is done only after the endoscopic procedure. We developed a Chan-Vese-based algorithm to segment fluorescence targets, and subsequent morphological operations to generate background, thus calculating target/background (T/B) ratios, potentially to provide real-time guidance for biopsy and endoscopic therapy. With an initial processing speed of 2 fps and by calculating the T/B ratio for each frame, our method provides quasireal-time quantification of the molecular probe labeling to the endoscopist. Furthermore, an automatic computer-aided diagnosis algorithm can be applied to the recorded endoscopic video, and the overall T/B ratio is calculated for each patient. The receiver operating characteristic curve was employed to determine the threshold for classification of HGD/EAC using leave-one-out cross-validation. With 92% sensitivity and 75% specificity to classify HGD/EAC, our automatic algorithm shows promising results for a surveillance procedure to help manage esophageal cancer and other cancers inspected by endoscopy.
Keywords: computer-aided diagnosis; esophageal cancer detection; fluorescence video processing; multimodal endoscopy; surgical guidance; target/background ratio.
Figures
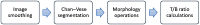
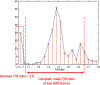
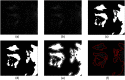



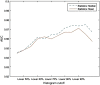
References
-
- Howlader N., et al. , SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2013, National Cancer Institute, Rockville, Maryland: (2006).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

