The protective effects of PCPA against monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension are mediated through the downregulation of NFAT-1 and NF-κB
- PMID: 28560440
- PMCID: PMC5466386
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3001
The protective effects of PCPA against monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension are mediated through the downregulation of NFAT-1 and NF-κB
Abstract
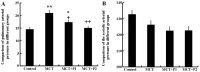
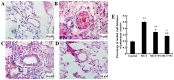
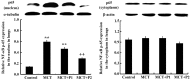
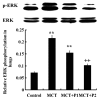
Inflammation and remodeling play a role in the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and nuclear factor of activated T cells-1 (NFAT-1) participate in inflammation and remodeling in a number of diseases. As a tryptophan hydroxylase inhibitor, 4-chloro-DL-phenylalanine (PCPA) had been reported to exert anti-inflammatory and remodeling effects. Therefore, we hypothesized that PCPA may attenuate monocrotaline (MCT)-induced PAH through the NFAT-1 and NF-κB signaling pathways. In order to confirm our hypothesis, we divided 68 Sprague-Dawley male rats into 4 groups as follows: the control, MCT, MCT + P1 and MCT + P2 groups. MCT was administered at a dose of 60 mg/kg once via intraperitoneal injection. PCPA was administered via intraperitoneal injection at a dose of 50 or 100 mg/kg once daily for 21 consecutive days. We then measured the hemodynamic index and morphological analysis was carried out on the lung tissues. Western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry were used to examine the levels of NFAT-1 and NF-κB p-65. The expression levels of phosphorylated inhibitor of NF-κB kinase (p-IKK), IKK, phosphorylated extracellular signal‑regulated kinase (p-ERK), ERK, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and inter-leukin-6 (IL-6) were examined by western blot analysis. MCT was found to significantly induce PAH, with inflammation and remodeling of the lung tissues. This was associatd with an increased expression of NFAT-1, p-IKK, p-ERK and nuclear p65. PCPA significantly attenuated MCT-induced inflammation and arterial remodeling, and decreased the expression of NFAT-1, as well as that of relevant proteins of the NF-κB signaling pathway. The above-mentioned findings suggest that the inhibitory effects of PCPA on MCT-induced inflammation and arterial remodeling are related to the downregulation of the NFAT-1 and NF-κB signaling pathways in rats with PAH.
Figures





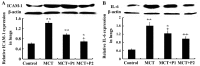
Similar articles
-
4-Chloro-DL-phenylalanine protects against monocrotaline‑induced pulmonary vascular remodeling and lung inflammation.Int J Mol Med. 2014 Feb;33(2):373-82. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1591. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Int J Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24337018
-
Calcineurin/NFAT Signaling Modulates Pulmonary Artery Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation, Migration and Apoptosis in Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Rats.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(1):172-189. doi: 10.1159/000492852. Epub 2018 Aug 22. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30134231
-
Pathophysiological roles of nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kB) in pulmonary arterial hypertension: effects of synthetic selective NF-kB inhibitor IMD-0354.Cardiovasc Res. 2013 Jul 1;99(1):35-43. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvt105. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Cardiovasc Res. 2013. PMID: 23631839
-
The role of nuclear factor of activated T cells in pulmonary arterial hypertension.Cell Cycle. 2017 Mar 19;16(6):508-514. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1281485. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Cell Cycle. 2017. PMID: 28103134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune and inflammatory mechanisms in pulmonary arterial hypertension.Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2012 Sep-Oct;55(2):218-28. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2012.07.006. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2012. PMID: 23009917 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Endothelial Dysfunction and Inflammation in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 9;22(22):12098. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212098. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34829978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PCPA protects against monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial remodeling in rats: potential roles of connective tissue growth factor.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 4;8(67):111642-111655. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22882. eCollection 2017 Dec 19. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29340081 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cell therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension: An update.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2022 Jun;41(6):692-703. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2022.02.020. Epub 2022 Mar 6. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2022. PMID: 35341679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative transcription profiling of mRNA and lncRNA in pulmonary arterial hypertension after C75 treatment.BMC Pulm Med. 2023 Jan 31;23(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12890-023-02334-6. BMC Pulm Med. 2023. PMID: 36717804 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effects of formononetin on the monocrotaline‑induced pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Mar;21(3):1192-1200. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.10911. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 31922224 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

