Cost per response for abatacept versus adalimumab in rheumatoid arthritis by ACPA subgroups in Germany, Italy, Spain, US and Canada
- PMID: 28560470
- PMCID: PMC5486786
- DOI: 10.1007/s00296-017-3739-9
Cost per response for abatacept versus adalimumab in rheumatoid arthritis by ACPA subgroups in Germany, Italy, Spain, US and Canada
Abstract
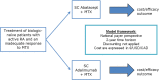
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder leading to disability and reduced quality of life. Effective treatment with biologic DMARDs poses a significant economic burden. The Abatacept versus Adalimumab Comparison in Biologic-Naïve RA Subjects with Background Methotrexate (AMPLE) trial was a head-to-head, randomized study comparing abatacept in serum anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA)-positive patients, with increasing efficacy across ACPA quartile levels. The aim of this study was to evaluate the cost per response accrued using abatacept versus adalimumab in ACPA-positive and ACPA-negative patients with RA from the health care perspective in Germany, Italy, Spain, the US and Canada. A cost-consequence analysis (CCA) was designed to compare the monthly costs per responding patient/patient in remission. Efficacy, safety and resource use inputs were based on the AMPLE trial. A one-way deterministic sensitivity analysis (OWSA) was also performed to assess the impact of model inputs on the results for total incremental costs. Cost per response in ACPA-positive patients favoured abatacept compared with adalimumab (ACR20, ACR90 and HAQ-DI). Subgroup analysis favoured abatacept with increasing stringency of response criteria and serum ACPA levels. Cost per remission (DAS28-CRP) favoured abatacept in ACPA-negative patients, while cost per CDAI and SDAI favoured abatacept in ACPA-positive patients. Abatacept was consistently favoured in ACPA-Q4 patients across all outcomes and countries. Cost savings were greater with abatacept when more stringent response criteria were applied and also with increasing ACPA levels, which could lead to a lower overall health care budget impact with abatacept compared with adalimumab.
Keywords: Biologic; Biomarker/prognostic factors; Cost-consequence analysis; Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs; Incremental cost analysis; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
Laure Weijers and Jason Foo have served as consultants to Bristol-Myers Squibb. Christoph Baerwald received honorarium for lectures and consultancies from Abbvie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Chugai, Medac, MSD, Pfizer, and Roche. Dr. Martin Bergman has received consulting and speaking fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Abbvie, Celgene, Genentech, Amgen, Janssen, Pfizer and Novartis. He is a shareholder of Merck, Pfizer and JNJ. Chad Patel is an employee and shareholder of Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Denis Choquette has received consulting and speaking fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Abbvie, Amgen, Celgene, Genentech, Amgen, Pfizer, Roche and Novartis.
Funding
This study was funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cost per response for abatacept versus adalimumab in patients with seropositive, erosive early rheumatoid arthritis in the US, Germany, Spain, and Canada.Rheumatol Int. 2019 Sep;39(9):1621-1630. doi: 10.1007/s00296-019-04352-2. Epub 2019 Jun 25. Rheumatol Int. 2019. PMID: 31240388
-
Cost-effectiveness of early treatment of ACPA-positive rheumatoid arthritis patients with abatacept.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018 May-Jun;36(3):448-454. Epub 2017 Dec 15. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29303709
-
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Abatacept Compared with Adalimumab on Background Methotrexate in Biologic-Naive Adult Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Poor Prognosis.Value Health. 2018 Feb;21(2):193-202. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2017.05.020. Epub 2017 Jul 1. Value Health. 2018. PMID: 29477401
-
Presence of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies is associated with better treatment response to abatacept but not to TNF inhibitors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2020 May-Jun;38(3):455-466. Epub 2019 Nov 16. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31770089
-
An overview of economic evaluations for drugs used in rheumatoid arthritis : focus on tumour necrosis factor-alpha antagonists.Drugs. 2005;65(4):473-96. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200565040-00004. Drugs. 2005. PMID: 15733011 Review.
Cited by
-
Value of Remission in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Targeted Review.Adv Ther. 2022 Jan;39(1):75-93. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01946-w. Epub 2021 Nov 17. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 34787822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Cost per Responder Model for Abatacept versus Adalimumab Among Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Seropositivity.Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2020 Oct 15;12:589-594. doi: 10.2147/CEOR.S263903. eCollection 2020. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2020. PMID: 33116698 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-consequence of abatacept as first-line therapy in Japanese rheumatoid arthritis patients using IORRA real-world data.PLoS One. 2022 Nov 16;17(11):e0277566. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277566. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36383610 Free PMC article.
-
Cost per response for abatacept versus adalimumab in patients with seropositive, erosive early rheumatoid arthritis in the US, Germany, Spain, and Canada.Rheumatol Int. 2019 Sep;39(9):1621-1630. doi: 10.1007/s00296-019-04352-2. Epub 2019 Jun 25. Rheumatol Int. 2019. PMID: 31240388
-
Effect of interleukin-6, -17, -21, -22, and -23 and STAT3 on signal transduction pathways and their inhibition in autoimmune arthritis.Immunol Res. 2021 Feb;69(1):26-42. doi: 10.1007/s12026-021-09173-9. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 33515210 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Singh JA, Saag KG, Bridges SL, Jr, Akl EA, Bannuru RR, Sullivan MC, Vaysbrot E, McNaughton C, Osani M, Shmerling RH, Curtis JR, Furst DE, Parks D, Kavanaugh A, O’Dell J, King C, Leong A, Matteson EL, Schousboe JT, Drevlow B, Ginsberg S, Grober J, St Clair EW, Tindall E, Miller AS, McAlindon T. 2015 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(1):1–26. doi: 10.1002/art.39480. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Landewe R, Breedveld FC, Buch M, Burmester G, Dougados M, Emery P, Gaujoux-Viala C, Gossec L, Nam J, Ramiro S, Winthrop K, de Wit M, Aletaha D, Betteridge N, Bijlsma JW, Boers M, Buttgereit F, Combe B, Cutolo M, Damjanov N, Hazes JM, Kouloumas M, Kvien TK, Mariette X, Pavelka K, van Riel PL, Rubbert-Roth A, Scholte-Voshaar M, Scott DL, Sokka-Isler T, Wong JB, van der Heijde D. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2013 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(3):492–509. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204573. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gaultney J, Benucci M, Iannazzo S, Nappi C, Sion K, Sabater FJ. Trial-based cost-effectiveness of abatacept for rheumatoid arthritis patients in Italy. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2015;23:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Khanna D, Massarotti E, Rosenblatt L, Budd D, Sabater J, Hebden T (2013) Comparison of cost-efficacy of subcutaneous abatacept versus adalimumab in the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Paper presented at the EULAR Annual Congress of Rheumatology, Madrid
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

