Design of a TW-SLIM Module for Dual Polarity Confinement, Transport, and Reactions
- PMID: 28560562
- PMCID: PMC5551421
- DOI: 10.1007/s13361-017-1680-5
Design of a TW-SLIM Module for Dual Polarity Confinement, Transport, and Reactions
Abstract
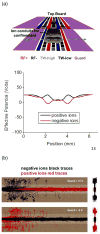
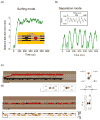
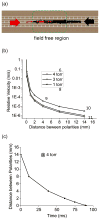
Here we describe instrumental approaches for performing dual polarity ion confinement, transport, ion mobility separations, and reactions in structures for lossless ion manipulations (SLIM). Previous means of ion confinement in SLIM, based upon rf-generated pseudopotentials and DC fields for lateral confinement, cannot trap ions of opposite polarity simultaneously. Here we explore alternative approaches to provide simultaneous lateral confinement of both ion polarities. Traveling wave ion mobility (IM) separations experienced in such SLIM cause ions of both polarities to migrate in the same directions and exhibit similar separations. The ion motion (and relative motion of the two polarities) under both surfing and IM separation conditions are discussed. In surfing conditions the two polarities are transported losslessly and non-reactively in their respective potential minima (higher absolute voltage regions confine negative polarities, and lower absolute potential regions are populated by positive polarities). In separation mode, where ions roll over an overtaking traveling wave, the two polarities can interact during the rollovers. Strategies to minimize overlap of the two ion populations to prevent reactive losses during separations are presented. A theoretical treatment of the time scales over which two populations (injected into a DC field-free region of the dual polarity SLIM device) interact is considered, and SLIM designs for allowing ion/ion interactions and other manipulations with dual polarities at 4 Torr are presented. Graphical Abstract ᅟ.
Keywords: Dual polarity; Ion mobility; Ion/ion reaction; SLIM; Traveling wave.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dual Polarity Ion Confinement and Mobility Separations.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2019 Jun;30(6):967-976. doi: 10.1007/s13361-019-02138-1. Epub 2019 Mar 4. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2019. PMID: 30834510 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Traveling Wave Ion Mobility Separations in Structures for Lossless Ion Manipulations.Anal Chem. 2015 Nov 17;87(22):11301-8. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02481. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Anal Chem. 2015. PMID: 26510005 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of applied fields for ion mobility separations in traveling wave based structures for lossless ion manipulations (SLIM).Int J Mass Spectrom. 2018 Jul;430:8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ijms.2018.03.006. Epub 2018 Mar 26. Int J Mass Spectrom. 2018. PMID: 31467482 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra-High Resolution Ion Mobility Separations Utilizing Traveling Waves in a 13 m Serpentine Path Length Structures for Lossless Ion Manipulations Module.Anal Chem. 2016 Sep 20;88(18):8957-64. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b01915. Epub 2016 Aug 26. Anal Chem. 2016. PMID: 27531027 Free PMC article.
-
LC-MS/MS systematic toxicological analysis: comparison of MS/MS spectra obtained with different instruments and settings.Clin Biochem. 2005 Apr;38(4):362-72. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2004.11.003. Clin Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15766737 Review.
Cited by
-
Resolving Power and Collision Cross Section Measurement Accuracy of a Prototype High-Resolution Ion Mobility Platform Incorporating Structures for Lossless Ion Manipulation.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2021 Apr 7;32(4):1126-1137. doi: 10.1021/jasms.1c00056. Epub 2021 Mar 18. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2021. PMID: 33734709 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Polarity Ion Confinement and Mobility Separations.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2019 Jun;30(6):967-976. doi: 10.1007/s13361-019-02138-1. Epub 2019 Mar 4. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2019. PMID: 30834510 Free PMC article.
-
SLIM Ultrahigh Resolution Ion Mobility Spectrometry Separations of Isotopologues and Isotopomers Reveal Mobility Shifts due to Mass Distribution Changes.Anal Chem. 2019 Sep 17;91(18):11952-11962. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b02808. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Anal Chem. 2019. PMID: 31450886 Free PMC article.
-
THE IMS PARADOX: A PERSPECTIVE ON STRUCTURAL ION MOBILITY-MASS SPECTROMETRY.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2021 May;40(3):280-305. doi: 10.1002/mas.21642. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2021. PMID: 32608033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traveling-Wave-Based Electrodynamic Switch for Concurrent Dual-Polarity Ion Manipulations in Structures for Lossless Ion Manipulations.Anal Chem. 2019 Nov 19;91(22):14712-14718. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b03987. Epub 2019 Oct 30. Anal Chem. 2019. PMID: 31621288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thomson JJ. Longmans, Green and Co; London: 1913.
-
- Osburn S, Ryzhov V. Ion–Molecule Reactions: Analytical and Structural Tool. Analytical Chemistry. 2013;85:769–778. - PubMed
-
- Gronert S, Li KH, Horiuchi M. Manipulating the fragmentation patterns of phosphopeptides via gas-phase boron derivatization: Determining phosphorylation sites in peptides with multiple serines. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2005;16:1905–1914. - PubMed
-
- Gao H, Petzold CJ, Leavell MD, Leary JA. Investigation of ion/molecule reactions as a quantification method for phosphorylated positional isomers: An FT-ICR approach. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2003;14:916–924. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

