Monitoring response to anti-angiogenic mTOR inhibitor therapy in vivo using 111In-bevacizumab
- PMID: 28560583
- PMCID: PMC5449352
- DOI: 10.1186/s13550-017-0297-9
Monitoring response to anti-angiogenic mTOR inhibitor therapy in vivo using 111In-bevacizumab
Abstract
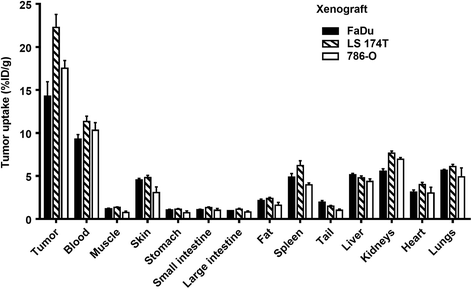
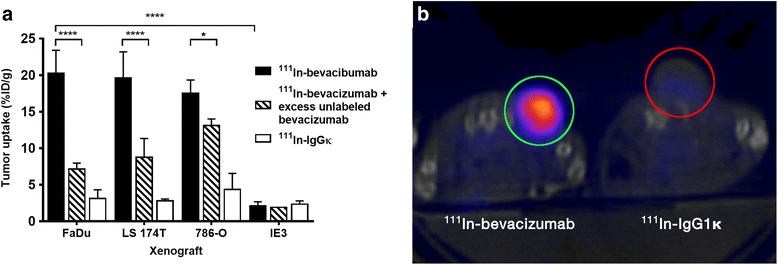
Background: The ability to image vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) could enable prospective, non-invasive monitoring of patients receiving anti-angiogenic therapy. This study investigates the specificity and pharmacokinetics of 111In-bevacizumab binding to VEGF and its use for assessing response to anti-angiogenic therapy with rapamycin. Specificity of 111In-bevacizumab binding to VEGF was tested in vitro with unmodified radiolabelled bevacizumab in competitive inhibition assays. Uptake of 111In-bevacizumab in BALB/c nude mice bearing tumours with different amounts of VEGF expression was compared to that of isotype-matched control antibody (111In-IgG1κ) with an excess of unlabelled bevacizumab. Intratumoural VEGF was evaluated using ELISA and Western blot analysis. The effect of anti-angiogenesis therapy was tested by measuring tumour uptake of 111In-bevacizumab in comparison to 111In-IgG1κ following administration of rapamycin to mice bearing FaDu xenografts. Uptake was measured using gamma counting of ex vivo tumours and effect on vasculature by using anti-CD31 microscopy.
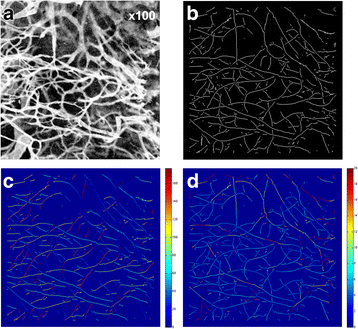
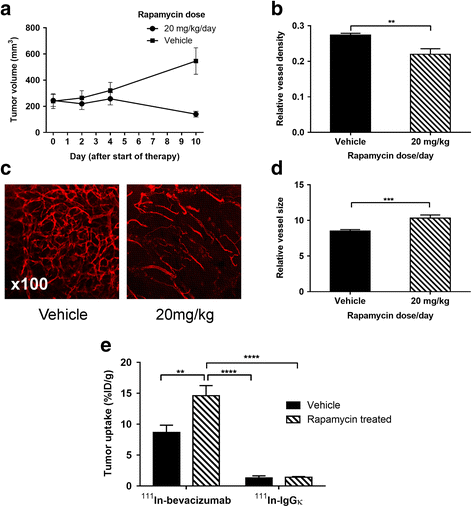
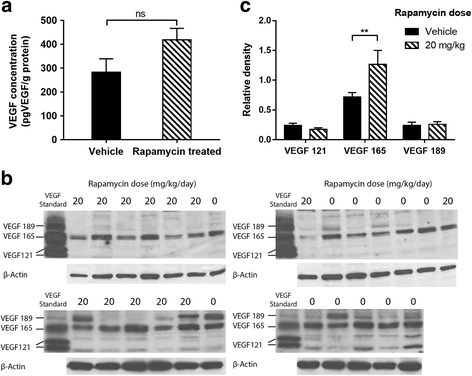
Results: Specific uptake of 111In-bevacizumab in VEGF-expressing tumours was observed. Rapamycin led to tumour growth delay associated with increased relative vessel size (8.5 to 10.3, P = 0.045) and decreased mean relative vessel density (0.27 to 0.22, P = 0.0015). Rapamycin treatment increased tumour uptake of 111In-bevacizumab (68%) but not 111In-IgGκ and corresponded with increased intratumoural VEGF165.
Conclusions: 111In-bevacizumab accumulates specifically in VEGF-expressing tumours, and changes after rapamycin therapy reflect changes in VEGF expression. Antagonism of mTOR may increase VEGF in vivo, and this new finding provides the basis to consider combination studies blocking both pathways and a way to monitor effects.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Bevacizumab; Cancer; Radionuclide; Rapamycin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
89Zr-bevacizumab PET of early antiangiogenic tumor response to treatment with HSP90 inhibitor NVP-AUY922.J Nucl Med. 2010 May;51(5):761-7. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.109.071043. Epub 2010 Apr 15. J Nucl Med. 2010. PMID: 20395337
-
Positron emission tomography imaging and biodistribution of vascular endothelial growth factor with 64Cu-labeled bevacizumab in colorectal cancer xenografts.Cancer Sci. 2011 Jan;102(1):117-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01763.x. Epub 2010 Nov 10. Cancer Sci. 2011. PMID: 21070475
-
Long-term treatment with anti-VEGF does not induce cell aging in primary retinal pigment epithelium.Exp Eye Res. 2018 Jun;171:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2018.03.002. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Exp Eye Res. 2018. PMID: 29522724
-
Biomarkers of anti-angiogenic therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC): original data and review of the literature.Z Gastroenterol. 2011 Oct;49(10):1398-406. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1281752. Epub 2011 Sep 30. Z Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21964893 Review.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) as a target of bevacizumab in cancer: from the biology to the clinic.Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(16):1845-57. doi: 10.2174/092986706777585059. Curr Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16842197 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of VEGF Receptors as Molecular Target in Nuclear Medicine for Cancer Diagnosis and Combination Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 3;13(5):1072. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051072. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33802353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutaminase inhibition with telaglenastat (CB-839) improves treatment response in combination with ionizing radiation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma models.Cancer Lett. 2021 Apr 1;502:180-188. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.12.038. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Cancer Lett. 2021. PMID: 33450358 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

