Beat frequency quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy for fast and calibration-free continuous trace-gas monitoring
- PMID: 28561065
- PMCID: PMC5460019
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms15331
Beat frequency quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy for fast and calibration-free continuous trace-gas monitoring
Abstract
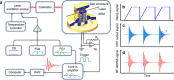
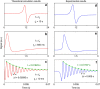
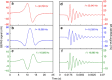
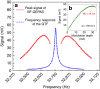
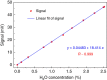
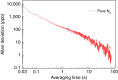
Quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy (QEPAS) is a sensitive gas detection technique which requires frequent calibration and has a long response time. Here we report beat frequency (BF) QEPAS that can be used for ultra-sensitive calibration-free trace-gas detection and fast spectral scan applications. The resonance frequency and Q-factor of the quartz tuning fork (QTF) as well as the trace-gas concentration can be obtained simultaneously by detecting the beat frequency signal generated when the transient response signal of the QTF is demodulated at its non-resonance frequency. Hence, BF-QEPAS avoids a calibration process and permits continuous monitoring of a targeted trace gas. Three semiconductor lasers were selected as the excitation source to verify the performance of the BF-QEPAS technique. The BF-QEPAS method is capable of measuring lower trace-gas concentration levels with shorter averaging times as compared to conventional PAS and QEPAS techniques and determines the electrical QTF parameters precisely.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Anthony K. W. et al. Methane emissions proportional to permafrost carbon thawed in Arctic lakes since the 1950s. Nat. Geosci. 9, 679–682 (2016).
-
- Ren W., Jiang W. & Tittel F. K. Single-QCL-based absorption sensor for simultaneous trace-gas detection of CH4 and N2O. Appl. Phys. B 117, 245–251 (2014).
-
- Kosterev A. A., Bakhirkin Y. A., Curl R. F. & Tittel F. K. Quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy. Opt. Lett. 27, 1902–1904 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

