The Upstream Determinants of Adult Obesity
- PMID: 28564658
- PMCID: PMC5644962
- DOI: 10.1159/000471489
The Upstream Determinants of Adult Obesity
Abstract
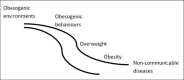
Over-consumption of high-energy foods and a lack of physical activity are the main behavioural risk factors for people to develop obesity. These behaviours are influenced by a range of individual-level factors which are nested within contexts that contain influencing characteristics further upstream. In this paper, we define these upstream determinants. We also provide a historical background, summarise the current evidence base regarding these determinants across various types of environments and put them in perspective.
Keywords: Adults; Dietary behaviours; Obesity; Physical activity; Upstream determinants.
© 2017 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger GmbH, Freiburg.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight. Factsheet. Updated June 2016. www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/ (last accessed May 19, 2017).
-
- Hu FB, Li TY, Colditz GA, Willett WC, Manson JE. Television watching and other sedentary behaviors in relation to risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus in women. JAMA. 2003;289:1785–1791. - PubMed
-
- Swinburn B, Sacks G, Hall K, McPherson K, Finegood D, Moodie M, et al. The global obesity pandemic: shaped by global drivers and local environments. Lancet. 2011;378:804–814. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical