A case report of tracheobronchitis by herpes simplex virus, type I
- PMID: 2856467
- PMCID: PMC4536714
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.1986.1.2.249
A case report of tracheobronchitis by herpes simplex virus, type I
Abstract
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection of the lung and lower respiratory tract has been thought to be a rare and fatal disease, usually in patients with immunosuppression, severe burns, or prolonged intubation. However, recently, increasing numbers of patients have been reported to have a localized infection and some of them have recovered without specific therapy.
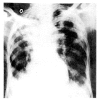
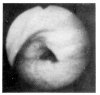
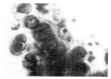
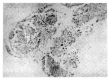
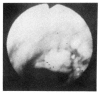
In Korea, there has been yet no proven case of HSV infection of the lower respiratory tract. Recently, we saw a case of localized HSV infection of the tracheobronchus. A 78-year-old male patient was admitted in acute respiratory failure, with COPD and old pulmonary trberculosis. After the clinical condition improved, a bronchoscopy was done which revealed a localized area of swelling, hyperemia, and mucosal irregularity at the lower trachea and right upper lobar bronchus. Bronchial brushing and biopsy showed typical cytologic changes including intranuclear inclusion body. Viral culture of a bronchial washing revealed a growth of HSV, type I. The patient died of unrelated, acute myocardial linfarction.
Figures
References
-
- Morgan HR, Finland M. Isolation of herpetic virus from a case of atypical pneumonia and erythema multiforme exudativum. Am J Med Sci. 1949;217:92. - PubMed
-
- Foley FD, Greenawald KA, Nash G. Herpes virus infection in burned patients. N Engl J Med. 1970;182:652. - PubMed
-
- Nash G, Foley FD. Herpetic infecton of the middle and lower respiratory tract. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970;54:857. - PubMed
-
- Nasn G. Necrotizing tracheobronchitis and bronchopneumonia consistent with herpetic infection. Human Pathol. 1972;3:283. - PubMed
-
- Douglas RG, Jr, Anderson MS, Weg JG. Herpes simplex virus pneumonia : Occurence in an allotransplanted lung. JAMA. 1969;210:902. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
