Main constituents of polyphenol complex from seagrasses of the genus Zostera, their antidiabetic properties and mechanisms of action
- PMID: 28565749
- PMCID: PMC5443317
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4217
Main constituents of polyphenol complex from seagrasses of the genus Zostera, their antidiabetic properties and mechanisms of action
Abstract
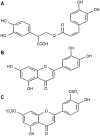
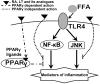
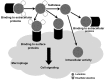
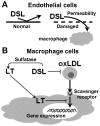
The present review analyzed the recent experimental studies of the alleviating activity of main constituents of the polyphenol complex from seagrasses of the genus Zostera, namely rosmarinic acid, luteolin and its sulfated derivatives, on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism disorders. A number of studies by our group and others, in which various experimental models of diabetes and hyperlipidemia were used, show a therapeutic action of the polyphenol complex and the abovementioned phenolic constituents, when applied separately and in combination. Based on the analysis of the results of these studies, the probable mechanisms of the therapeutic action of these compounds in diabetes and hyperlipidemia were proposed.
Keywords: diabetes; flavonoids; hyperlipidemia; luteolin; metabolic syndrome; rosmarinic acid.
Figures


References
-
- Finucane MM, Danaei G, Ezzati M. Bayesian estimation of population-level trends in measures of health status. Statistical Sci. 2014;29:18–25. doi: 10.1214/13-STS427. - DOI
-
- Krylova NV, Popov AM, Leonova GN. Antioxidants as potential antiviral agents for flavivirus infections (Review) Antibiotiki i Khimioterapiya. 2016;61:25–31. (In Russian) - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
