An exploratory study into the role of miR-204-5p in pregnancy-induced hypertension
- PMID: 28565757
- PMCID: PMC5443271
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4212
An exploratory study into the role of miR-204-5p in pregnancy-induced hypertension
Abstract
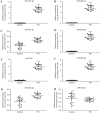
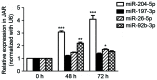
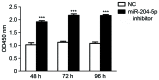
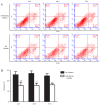
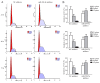
The molecular mechanism that leads to pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH), a pregnancy-specific syndrome, remains poorly understood. It has been suggested that microRNAs (miRNAs) may be potentially useful biomarkers for severe preeclampsia (PE), which is an important condition associated with PIH. The aim of the present study was to identify miR-204 by verifying differentially expressed serum miRNAs in patients with PIH during pregnancy compared with normal controls. Subsequently, the effects of miR-204 on proliferation and apoptosis of human choriocarcinoma (JAR) cells in hypoxic microenvironment were investigated. Previous studies indicated a number of miRNA candidates and the present study validated the expression of eight miRNAs in serum samples using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). A higher expression of miR-204 was identified in patients with PIH. To assess the impact of miR-204 inhibition on hypoxic JAR cells function in vitro, cell proliferation was detected using a Cell Counting Kit-8 assay. The rate of apoptosis and cell cycle progression was then examined by flow cytometry. RT-qPCR confirmed that serum miR-204-5p is more highly expressed in patients with PIH. Further statistical analysis indicated that the survival ratio of JAR cells in hypoxic microenvironments was increased in the miR-204-5p inhibitor group. However, the miR-204-5p inhibitor protected hypoxic JAR cells from apoptosis. The analysis of cell-cycle status demonstrated that the percentage of cells in the G2/G1 phase was larger compared with the control group. The results of the present study suggest that low levels of miR-204-5p may increase cell proliferation and reduce cell apoptosis with cell cycle changes in vitro. Therefore, serum miR-204-5p may be used as a notable biomarker for the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of PIH.
Keywords: cell apoptosis; cell proliferation; miR-204-5p; preeclampsia; pregnancy-induced hypertension.
Figures
References
-
- Magee LA, Pels A, Helewa M, Rey E, von Dadelszen P. Canadian Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy Working Group: Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: Executive summary. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2014;36:416–441. doi: 10.1016/S1701-2163(15)30588-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Magee LA, Helewa M, Moutquin JM, von Dadelszen P. Hypertension Guideline Committee; Strategic Training Initiative in Research in the Reproductive Health Sciences (STIRRHS) Scholars: Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2008;30:S1–S48. doi: 10.1016/S1701-2163(16)32776-1. (Suppl 3) - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
