Clinical study on the association between pregnancy-induced hypertension and insulin resistance
- PMID: 28565809
- PMCID: PMC5443191
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4169
Clinical study on the association between pregnancy-induced hypertension and insulin resistance
Abstract
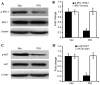
The aim of the present study was to explore the association between pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) and insulin resistance (IR). A total of 50 cases of PIH and 50 healthy pregnant women with a similar gestational age were enrolled. The hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp technique was used to evaluate the degree of IR and all 100 subjects were divided into an IR and a non-IR group accordingly. Subsequently, the correlation between the systolic or diastolic blood pressure was assessed; furthermore, a homeostasis model assessment of IR (HOMA-IR), a HOMA of the insulin sensitivity index (HOMA-ISI) and a HOMA of β cell function (HOMA-β%) were performed. Moreover, the effect of IR on PIH was assessed and the protein expression of insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1, phosphorylated (p)-IRS-1, AKT and p-AKT were detected in the placental plasma by western blot analysis. The results showed that in the PIH group, the p-IRS-1/IRS-1 and p-AKT/AKT ratios were decreased compared with those in the control group. Blood flow parameters, including perfusion index, retinal resistive index and systolic maximum velocity/end-diastolic velocity ratio in the IR group were higher, while time averaged velocity was lower compared with that in the non-IR group. Furthermore, the HOMA-ISI and HOMA-β% were decreased, while the HOMA-IR was increased in the PIH group compared to that in the control group; alongside the blockage of the insulin signaling pathway, these factors may therefore cause PIH. The present study may provide novel therapeutic approaches for PIH.
Keywords: HOMA-IR; HOMA-ISI; HOMA-β%; insulin resistance; pregnancy-induced hypertension.
Figures
References
-
- Salge AK, Xavier RM, Ramalho WS, Rocha EL, Coelho AS, Guimarães JV, Siqueira KM, Abdalla DR, Michelin MA, Murta EF. Placental and umbilical cord macroscopic changes associated with fetal and maternal events in the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 2013;40:198–202. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
