An Expanded Genome-Wide Association Study of Type 2 Diabetes in Europeans
- PMID: 28566273
- PMCID: PMC5652602
- DOI: 10.2337/db16-1253
An Expanded Genome-Wide Association Study of Type 2 Diabetes in Europeans
Abstract
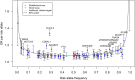
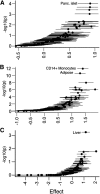
To characterize type 2 diabetes (T2D)-associated variation across the allele frequency spectrum, we conducted a meta-analysis of genome-wide association data from 26,676 T2D case and 132,532 control subjects of European ancestry after imputation using the 1000 Genomes multiethnic reference panel. Promising association signals were followed up in additional data sets (of 14,545 or 7,397 T2D case and 38,994 or 71,604 control subjects). We identified 13 novel T2D-associated loci (P < 5 × 10-8), including variants near the GLP2R, GIP, and HLA-DQA1 genes. Our analysis brought the total number of independent T2D associations to 128 distinct signals at 113 loci. Despite substantially increased sample size and more complete coverage of low-frequency variation, all novel associations were driven by common single nucleotide variants. Credible sets of potentially causal variants were generally larger than those based on imputation with earlier reference panels, consistent with resolution of causal signals to common risk haplotypes. Stratification of T2D-associated loci based on T2D-related quantitative trait associations revealed tissue-specific enrichment of regulatory annotations in pancreatic islet enhancers for loci influencing insulin secretion and in adipocytes, monocytes, and hepatocytes for insulin action-associated loci. These findings highlight the predominant role played by common variants of modest effect and the diversity of biological mechanisms influencing T2D pathophysiology.
© 2017 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures

Comment in
-
Give GWAS a Chance.Diabetes. 2017 Nov;66(11):2741-2742. doi: 10.2337/dbi17-0026. Diabetes. 2017. PMID: 29061660 No abstract available.
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015;386:743–800 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mahajan A, Go MJ, Zhang W, et al.; DIAbetes Genetics Replication And Meta-analysis (DIAGRAM) Consortium; Asian Genetic Epidemiology Network Type 2 Diabetes (AGEN-T2D) Consortium; South Asian Type 2 Diabetes (SAT2D) Consortium; Mexican American Type 2 Diabetes (MAT2D) Consortium; Type 2 Diabetes Genetic Exploration by Nex-generation sequencing in muylti-Ethnic Samples (T2D-GENES) Consortium . Genome-wide trans-ancestry meta-analysis provides insight into the genetic architecture of type 2 diabetes susceptibility. Nat Genet 2014;46:234–244 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Morris AP, Voight BF, Teslovich TM, et al.; Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium; Meta-Analyses of Glucose and Insulin-related traits Consortium (MAGIC) Investigators; Genetic Investigation of ANthropometric Traits (GIANT) Consortium; Asian Genetic Epidemiology Network–Type 2 Diabetes (AGEN-T2D) Consortium; South Asian Type 2 Diabetes (SAT2D) Consortium; DIAbetes Genetics Replication And Meta-analysis (DIAGRAM) Consortium . Large-scale association analysis provides insights into the genetic architecture and pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 2012;44:981–990 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG000040/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD018522/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA167552/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG033067/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0601261/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M501633/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK093757/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007417/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK073490/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 098017/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 DK058845/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RG/08/008/25291/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- U01 DK085545/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK106236/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HG065403/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098032/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG000376/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG008724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 DK105535/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101478/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK046200/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028555/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12015/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- ZIA HG000024/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 DK088389/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK080140/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA186107/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085526/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M501633/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/14/5/30893/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MR/K007017/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_13040/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL087641/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG010175/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
- Archivio Istituzionale della Ricerca Unimi - Access Free Full Text
- Enlighten: Publications, University of Glasgow - Access Free Full Text
- Europe PubMed Central
- Ovid Technologies, Inc.
- PubMed Central
- Silverchair Information Systems
- Spiral, Imperial College Digital Repository
- eScholarship, University of California - Access Free Full Text
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

