Enzymatic lipid oxidation by eosinophils propagates coagulation, hemostasis, and thrombotic disease
- PMID: 28566277
- PMCID: PMC5502424
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20161070
Enzymatic lipid oxidation by eosinophils propagates coagulation, hemostasis, and thrombotic disease
Erratum in
-
Correction: Enzymatic lipid oxidation by eosinophils propagates coagulation, hemostasis, and thrombotic disease.J Exp Med. 2018 Mar 5;215(3):1003. doi: 10.1084/jem.2016107002142018c. Epub 2018 Feb 20. J Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 29463570 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
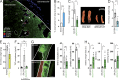
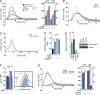
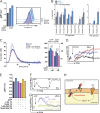
Blood coagulation is essential for physiological hemostasis but simultaneously contributes to thrombotic disease. However, molecular and cellular events controlling initiation and propagation of coagulation are still incompletely understood. In this study, we demonstrate an unexpected role of eosinophils during plasmatic coagulation, hemostasis, and thrombosis. Using a large-scale epidemiological approach, we identified eosinophil cationic protein as an independent and predictive risk factor for thrombotic events in humans. Concurrent experiments showed that eosinophils contributed to intravascular thrombosis by exhibiting a strong endogenous thrombin-generation capacity that relied on the enzymatic generation and active provision of a procoagulant phospholipid surface enriched in 12/15-lipoxygenase-derived hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid-phosphatidylethanolamines. Our findings reveal a previously unrecognized role of eosinophils and enzymatic lipid oxidation as regulatory elements that facilitate both hemostasis and thrombosis in response to vascular injury, thus identifying promising new targets for the treatment of thrombotic disease.
© 2017 Uderhardt et al.
Figures

References
-
- Assarsson E., Lundberg M., Holmquist G., Björkesten J., Thorsen S.B., Ekman D., Eriksson A., Rennel Dickens E., Ohlsson S., Edfeldt G., et al. 2014. Homogenous 96-plex PEA immunoassay exhibiting high sensitivity, specificity, and excellent scalability. PLoS One. 9:e95192 10.1371/journal.pone.0095192 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clark S.R., Thomas C.P., Hammond V.J., Aldrovandi M., Wilkinson G.W., Hart K.W., Murphy R.C., Collins P.W., and O’Donnell V.B.. 2013. Characterization of platelet aminophospholipid externalization reveals fatty acids as molecular determinants that regulate coagulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 110:5875–5880. 10.1073/pnas.1222419110 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

