Caspofungin Increases Fungal Chitin and Eosinophil and γδ T Cell-Dependent Pathology in Invasive Aspergillosis
- PMID: 28566368
- PMCID: PMC5508594
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700078
Caspofungin Increases Fungal Chitin and Eosinophil and γδ T Cell-Dependent Pathology in Invasive Aspergillosis
Abstract
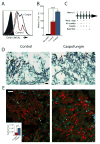
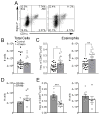
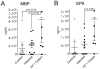
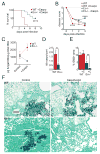
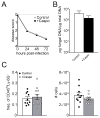
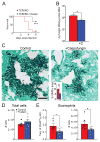
The polysaccharide-rich fungal cell wall provides pathogen-specific targets for antifungal therapy and distinct molecular patterns that stimulate protective or detrimental host immunity. The echinocandin antifungal caspofungin inhibits synthesis of cell wall β-1,3-glucan and is used for prophylactic therapy in immune-suppressed individuals. However, breakthrough infections with fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus are associated with caspofungin prophylaxis. In this study, we report in vitro and in vivo increases in fungal surface chitin in A. fumigatus induced by caspofungin that was associated with airway eosinophil recruitment in neutropenic mice with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IA). More importantly, caspofungin treatment of mice with IA resulted in a pattern of increased fungal burden and severity of disease that was reversed in eosinophil-deficient mice. Additionally, the eosinophil granule proteins major basic protein and eosinophil peroxidase were more frequently detected in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of lung transplant patients diagnosed with IA that received caspofungin therapy when compared with azole-treated patients. Eosinophil recruitment and inhibition of fungal clearance in caspofungin-treated mice with IA required RAG1 expression and γδ T cells. These results identify an eosinophil-mediated mechanism for paradoxical caspofungin activity and support the future investigation of the potential of eosinophil or fungal chitin-targeted inhibition in the treatment of IA.
Copyright © 2017 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures

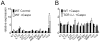
Similar articles
-
The Aspergillus fumigatus CrzA Transcription Factor Activates Chitin Synthase Gene Expression during the Caspofungin Paradoxical Effect.mBio. 2017 Jun 13;8(3):e00705-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00705-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28611248 Free PMC article.
-
Lung eosinophil recruitment in response to Aspergillus fumigatus is correlated with fungal cell wall composition and requires γδ T cells.Microbes Infect. 2017 Jul-Aug;19(7-8):422-431. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2017.05.001. Epub 2017 May 25. Microbes Infect. 2017. PMID: 28552410 Free PMC article.
-
The Paradoxical Effect of Echinocandins in Aspergillus fumigatus Relies on Recovery of the β-1,3-Glucan Synthase Fks1.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Jan 24;61(2):e01690-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01690-16. Print 2017 Feb. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 27872079 Free PMC article.
-
Echinocandins for the Treatment of Invasive Aspergillosis: from Laboratory to Bedside.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Jul 25;63(8):e00399-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00399-19. Print 2019 Aug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31138565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Echinocandin antifungal drugs in fungal infections: a comparison.Drugs. 2011 Jan 1;71(1):11-41. doi: 10.2165/11585270-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2011. PMID: 21175238 Review.
Cited by
-
Acidic Mammalian Chitinase Negatively Affects Immune Responses during Acute and Chronic Aspergillus fumigatus Exposure.Infect Immun. 2018 Jun 21;86(7):e00944-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00944-17. Print 2018 Jul. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 29712728 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of the Aspergillus fumigatus Cell Wall Modification and Ensuing Human Dendritic Cell Responses by β-(1,3)-Glucan Synthase Inhibitors-Caspofungin and Enfumafungin.Mycopathologia. 2024 Sep 20;189(5):86. doi: 10.1007/s11046-024-00894-7. Mycopathologia. 2024. PMID: 39302505
-
Survival Factor A (SvfA) Contributes to Aspergillus nidulans Pathogenicity.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Jan 21;9(2):143. doi: 10.3390/jof9020143. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836258 Free PMC article.
-
Chitin Biosynthesis in Aspergillus Species.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Jan 6;9(1):89. doi: 10.3390/jof9010089. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36675910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host response to pulmonary fungal infections: A highlight on cell-driven immunity to Cryptococcus species and Aspergillus fumigatus.Curr Pharmacol Rep. 2017 Dec;3(6):335-345. doi: 10.1007/s40495-017-0111-4. Epub 2017 Oct 14. Curr Pharmacol Rep. 2017. PMID: 29430385 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ostrosky-Zeichner L, Casadevall A, Galgiani JN, Odds FC, Rex JH. An insight into the antifungal pipeline: selected new molecules and beyond. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9:719–727. - PubMed
-
- Dockrell DH. Salvage therapy for invasive aspergillosis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008;61(Suppl 1):i41–44. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

