An Autopsy Case of Respiratory Failure Induced by Repetitive Cervical Spinal Cord Damage due to Abnormal Movement of the Neck in Athetoid Cerebral Palsy
- PMID: 28566610
- PMCID: PMC5498211
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.56.7411
An Autopsy Case of Respiratory Failure Induced by Repetitive Cervical Spinal Cord Damage due to Abnormal Movement of the Neck in Athetoid Cerebral Palsy
Abstract
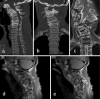
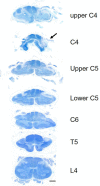
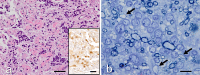
We herein report the clinical and autopsy findings of a 48-year-old right-handed man with athetoid cerebral palsy who suffered from cervical myelopathy due to abnormal neck movement, and who died of respiratory failure. Pathologically, the external appearance of the ventral surface of the cervical spinal cord revealed a linear indentation running obliquely at the level between the C4 and C5 segments. In the most severely compressed lesion, the gray matter was predominantly affected and severely atrophic. Microscopically, clusters of oligodendrocytes associated with thinly myelinated axons were also observed in the lateral funiculus. The latter findings are unique, and could be interpreted as regenerative and/or restorative phenomena of the central nervous system following chronic repetitive spinal cord compression.
Keywords: athetoid cerebral palsy; cervical spondylosis; myelopathy; neuropathological finding; oligodendrocyte; respiratory failure.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cervical myelo-radiculopathy in athetoid cerebral palsy.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1997;116(1-2):116-8. doi: 10.1007/BF00434115. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1997. PMID: 9006780
-
Laminoplasty with lateral mass screw fixation for cervical spondylotic myelopathy in patients with athetoid cerebral palsy: A retrospective study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Sep;95(39):e5033. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005033. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27684879 Free PMC article.
-
[Peri-operative treatment with botulinum A toxin prior to posterior cervical decompression in a case with cervical spondylosis caused by spasmodic torticollis secondary to cerebral palsy].No Shinkei Geka. 2003 Sep;31(9):1015-20. No Shinkei Geka. 2003. PMID: 14513786 Japanese.
-
[Combined anterior-posterior arthrodesis en patient with athetoid cerebral palsy who developed spondylotic cervical mielopathy. Case report and review of literature].Neurocirugia (Astur). 2011 Jun;22(3):245-50. Neurocirugia (Astur). 2011. PMID: 21743945 Review. Spanish.
-
Acquired spinal cord lesion associated with os odontoideum causing deterioration in dystonic cerebral palsy: case report and review of the literature.Dev Med Child Neurol. 1998 Mar;40(3):195-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1998.tb15447.x. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1998. PMID: 9566658 Review.
Cited by
-
What is the best treatment option for cervical spinal cord injury by os odontoideum in a patient with athetoid dystonic cerebral palsy?J Spinal Cord Med. 2021 Nov;44(6):1019-1023. doi: 10.1080/10790268.2019.1706289. Epub 2020 Jan 9. J Spinal Cord Med. 2021. PMID: 31916917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bax M, Goldstein M, Rosenbaum P, et al. . Proposed definition and classification of cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 47: 571-576, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Fuji T, Yonenobu K, Fujiwara K, et al. . Cervical radiculopathy or myelopathy secondary to athetoid cerebral palsy. J Bone Joint Surg 69: 815-821, 1987. - PubMed
-
- Nokura K, Hashizume Y, Inagaki T, Ojika K, Yamamoto M. Clinical and pathological study of myelopathy accompanied with cervical spinal canal stenosis--with special reference to complication of mental retardation or cerebral palsy. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 33: 121-129, 1993(in Japanese, Abstract in English). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

