Greater muscle damage in athletes with ACTN3 R577X (RS1815739) gene polymorphism after an ultra-endurance race: a pilot study
- PMID: 28566803
- PMCID: PMC5424449
- DOI: 10.5114/biolsport.2017.64583
Greater muscle damage in athletes with ACTN3 R577X (RS1815739) gene polymorphism after an ultra-endurance race: a pilot study
Abstract
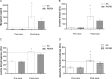
In this study, we aimed to investigate the influence of ACTN3 R577X gene polymorphism on muscle damage responses in athletes competing in an ultra-endurance race. Twenty moderate to well-trained ultra-runners who had entered in an official 37.1 km adventure race (22.1 km mountain biking, 10.9 km trekking, 4.1 km water trekking, 30 m rope course, and orienteering) volunteered for the study. Blood samples were collected for genotyping and analysis of muscle protein levels before and after the race. Percentage changes (pre- to post-race) of serum myoglobin [XX = 5,377% vs. RX/RR = 1,666%; P = 0.005, effect size (ES) = 1.73], creatine kinase (XX = 836.5% vs. RX/RR = 455%; P = 0.04, ES = 1.29), lactate dehydrogenase (XX = 82% vs. RX/RR = 65%; P = 0.002, ES = 1.61), and aspartate aminotransferase (XX = 148% vs. RX/RR = 75%; P = 0.02, ES = 1.77) were significantly greater for XX than RX/RR genotypes. ES analysis confirmed a large magnitude of muscle damage in XX genotype ultra-runners. Therefore, athletes with the ACTN3 577XX genotype experienced more muscle damage after an adventure race. This suggests that ultra-runners with alpha-actinin-3 deficiency may be more susceptible to rhabdomyolysis and associated health complications during ultra-endurance competitions.
Keywords: ACTN3; Adventure race; Genetics; Muscle damage; Ultra-endurance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Levada-Pires AC, Fonseca CE, Hatanaka E, Alba-Loureiro T, D’Angelo A, Velhote FB, et al. The effect of an adventure race on lymphocyte and neutrophil death. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010;109:447–53. - PubMed
-
- Lucas SJ, Anglem N, Roberts WS, Anson JG, Palmer CD, Walker RJ, et al. Intensity and physiological strain of competitive ultra-endurance exercise in humans. J Sports Sci. 2008;26:477–89. - PubMed
-
- Wichardt E, Mattsson CM, Ekblom B, Henriksson-Larsen K. Rhabdomyolysis/myoglobinemia and NSAID during 48 h ultra-endurance exercise (adventure racing) Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011;111:1541–4. - PubMed
-
- Baur DA, Bach CW, Hyder WJ, Ormsbee MJ. Fluid retention, muscle damage, and altered body composition at the Ultraman triathlon. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2016;116:447–58. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
