The Current Status of Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Korea: Based on Year 2014 Cohort of Korean Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (K-PCI) Registry
- PMID: 28567083
- PMCID: PMC5449527
- DOI: 10.4070/kcj.2017.0071
The Current Status of Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Korea: Based on Year 2014 Cohort of Korean Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (K-PCI) Registry
Abstract
Background and objectives: Although several multicenter registries have evaluated percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) procedures in Korea, those databases have been limited by non-standardized data collection and lack of uniform reporting methods. We aimed to collect and report data from a standardized database to analyze PCI procedures throughout the country.
Materials and methods: Both clinical and procedural data, as well as clinical outcomes data during hospital stay, were collected based on case report forms that used a standard set of 54 data elements. This report is based on 2014 Korean PCI registry cohort data.
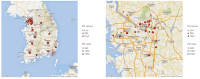
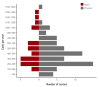
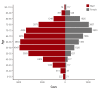
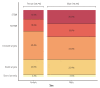
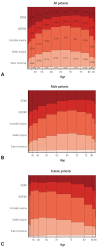
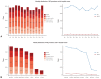
Results: A total of 92 hospitals offered data on 44967 PCI procedures. The median age was 66.0 interquartile range 57.0-74.0 years, and 70.3% were men. Thirty-eight percent of patients presented with acute myocardial infarction and one-third of all PCI procedures were performed in an urgent or emergency setting. Non-invasive stress tests were performed in 13.9% of cases, while coronary computed tomography angiography was used in 13.7% of cases prior to PCI. Radial artery access was used in 56.1% of all PCI procedures. Devices that used PCI included drug-eluting stent, plain old balloon angioplasty, drug-eluting balloon, and bare-metal stent (around 91%, 19%, 6%, and 1% of all procedures, respectively). The incidences of in-hospital death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, and stroke were 2.3%, 1.6%, and 0.2%, respectively.
Conclusion: These data may provide an overview of the current PCI practices and in-hospital outcomes in Korea and could be used as a foundation for developing treatment guidelines and nationwide clinical research.
Keywords: Percutaneous coronary intervention; Registry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Amsterdam EA, Wenger NK, Brindis RG, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2014;130:2354–2394. - PubMed
-
- Authors/Task Force members. Windecker S, Kolh P, et al. 2014 ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization: the task force on myocardial revascularization of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Developed with the special contribution of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI) Eur Heart J. 2014;35:2541–2619. - PubMed
-
- Levine GN, Bates ER, Blankenship JC, et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA/SCAI guideline for percutaneous coronary intervention: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines and the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions. Circulation. 2011;124:e574–e651. - PubMed
-
- O'Gara P, Kushner F, Ascheim D, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61:e78–e140. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

