Cerebral haemodynamics in early puerperium: A prospective study
- PMID: 28567105
- PMCID: PMC5438056
- DOI: 10.1177/1742271X17690942
Cerebral haemodynamics in early puerperium: A prospective study
Abstract
Aim: Prospective study on 900 consecutive puerperae to assess normal values and range of the blood flow velocity in the middle cerebral artery in both hemispheres.
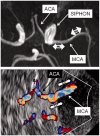
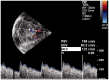
Material and method: M1 and M2 segments of both middle cerebral arteries were assessed in all subjects within 96 hours of delivery. Mean flow velocity was recorded after adjusting for insonation angle. Lindegaard index (LI = middle cerebral artery-Internal Carotid Artery mean flow velocity ratio) was calculated whenever the mean flow velocity exceeded 100 cm/second. Asymmetry indexes were calculated inter hemispherically for M1 and M2 segments separately.
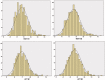
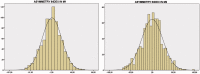
Results: Mean flow velocities were 74 ± 17 and 72 ± 17 in right and 73 ± 17 and 72 ± 17 cm/second in the left M1 and M2, respectively. A total of 136 subjects (12.1%) exceeded the threshold of 100 cm/second, but LI was consistently <3 in all of them. Mean flow velocity was inversely and independently correlated to haemoglobin levels and to parity. Mean asymmetry indexes were 0.25 ± 23 in M1 and 0.45 ± 25 in M2.
Conclusion: Mean flow velocity in the middle cerebral artery of healthy subjects in early puerperium is higher than in age-matched non-puerperal women and may exceed the threshold of 100 cm/second with no evidence of intracranial spasm, because of blood loss during delivery. Mean flow velocity is independently correlated with parity. Right-to-left mean flow velocity asymmetry may reach 50% as a consequence of a transient imbalance in vascular tone regulation.
Keywords: Mean flow velocity; asymmetry index; middle cerebral artery; puerperium.
Figures
References
-
- Akhter T, Larsson A, Larsson M, et al. Artery wall layer dimensions during normal pregnancy: a longitudinal study using noninvasive high-frequency ultrasound. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2013; 304: H229–H234. - PubMed
-
- Skeik N, Porten BR, Kadkhodayan Y, et al. Postpartum reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: review and analysis of the current data. Vasc Med 2015; 20: 256–265. - PubMed
-
- Demarin V, Rundek T, Hodek B. Maternal cerebral circulation in normal and abnormal pregnancies. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1997; 76: 619–624. - PubMed
-
- Williams K, Wilson S. Persistance of cerebral hemodynamic changesin patients with eclampsia: a report of three cases. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999; 181: 1162–1165. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
