Treatment of Subacromial Impingement Syndrome: Platelet-Rich Plasma or Exercise Therapy? A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 28567426
- PMCID: PMC5439655
- DOI: 10.1177/2325967117702366
Treatment of Subacromial Impingement Syndrome: Platelet-Rich Plasma or Exercise Therapy? A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Subacromial impingement syndrome (SAIS) is the most common disorder of the shoulder. The evidence for the effectiveness of treatment options is inconclusive and limited. Therefore, there is a need for more evidence in this regard, particularly for long-term outcomes.
Hypothesis: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) would be an effective method in treating subacromial impingement.
Study design: Randomized controlled trial; Level of evidence, 1.
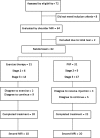
Methods: This was a single-blinded randomized clinical trial with 1-, 3-, and 6-month follow-up. Sixty-two patients were randomly placed into 2 groups, receiving either PRP or exercise therapy. The outcome parameters were pain, shoulder range of motion (ROM), muscle force, functionality, and magnetic resonance imaging findings.
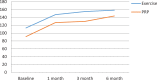
Results: Both treatment options significantly reduced pain and increased shoulder ROM compared with baseline measurements. Both treatments also significantly improved functionality. However, the treatment choices were not significantly effective in improving muscle force. Trend analysis revealed that in the first and third months, exercise therapy was superior to PRP in pain, shoulder flexion and abduction, and functionality. However, in the sixth month, only shoulder abduction and total Western Ontario Rotator Cuff score were significantly different between the 2 groups.
Conclusion: Both PRP injection and exercise therapy were effective in reducing pain and disability in patients with SAIS, with exercise therapy proving more effective.
Keywords: PRP; exercise therapy; subacromial impingement syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
One or more of the authors has declared the following potential conflict of interest or source of funding: This study was funded and supported by the Iran University of Medical Sciences grant 92-01-30-21391.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Clinical Effects of Additional Platelet-Rich Plasma Application to Exercise Therapy in Patients with Subacromial Impingement Syndrome: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial.Orthop J Sports Med. 2024 Oct 8;12(10):23259671241276368. doi: 10.1177/23259671241276368. eCollection 2024 Oct. Orthop J Sports Med. 2024. PMID: 39385967 Free PMC article.
-
Is there evidence in favor of surgical interventions for the subacromial impingement syndrome?Clin J Sport Med. 2013 Sep;23(5):406-7. doi: 10.1097/01.jsm.0000433152.74183.53. Clin J Sport Med. 2013. PMID: 23989383
-
Platelet-rich plasma injections in the treatment of chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial with 1-year follow-up.Am J Sports Med. 2013 Nov;41(11):2609-16. doi: 10.1177/0363546513496542. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Am J Sports Med. 2013. PMID: 23893418 Clinical Trial.
-
Nonoperative Treatment of Rotator Cuff Disease With Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials.Arthroscopy. 2019 May;35(5):1584-1591. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2018.10.115. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Arthroscopy. 2019. PMID: 31000394
-
Effect of supervised physiotherapy versus home exercise program in patients with subacromial impingement syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Phys Ther Sport. 2020 Jan;41:34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ptsp.2019.11.003. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Phys Ther Sport. 2020. PMID: 31726386
Cited by
-
CORR Synthesis: What Is the Role of Platelet-rich Plasma Injection in the Treatment of Tendon Disorders?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020 Aug;478(8):1817-1824. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000001312. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020. PMID: 32732562 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Can platelet-rich plasma injections provide better pain relief and functional outcomes in persons with common shoulder diseases: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Clin Shoulder Elb. 2022 Mar;25(1):73-89. doi: 10.5397/cise.2021.00353. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Clin Shoulder Elb. 2022. PMID: 34823313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injections for rotator cuff tendinopathy: a comparative study with up to 18-month follow-up.Clin Shoulder Elb. 2022 Mar;25(1):28-35. doi: 10.5397/cise.2021.00486. Epub 2022 Jan 25. Clin Shoulder Elb. 2022. PMID: 35086189 Free PMC article.
-
Role of platelet rich plasma in rotator cuff tendinopathy- clinical application and review of literature.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2019 Mar-Apr;10(2):244-247. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2018.10.014. Epub 2018 Oct 21. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2019. PMID: 30828186 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
The role of platelet-rich plasma in shoulder pathologies: a critical review of the literature.EFORT Open Rev. 2023 Apr 25;8(4):213-222. doi: 10.1530/EOR-22-0104. EFORT Open Rev. 2023. PMID: 37097022 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andia I, Latorre P, Gomez M, Burgos-Alonso N, Abate M, Maffulli N. Platelet-rich plasma in the conservative treatment of painful tendinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled studies. Br Med Bull. 2014;110:99–115. - PubMed
-
- Balasubramaniam U, Dissanayake R, Annabell L. Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma injections in pain associated with chronic tendinopathy: a systematic review. Phys Sportsmed. 2015;43:253–261. - PubMed
-
- Barber FA, Hrnack SA, Snyder SJ, Hapa O. Rotator cuff repair healing influenced by platelet-rich plasma construct augmentation. Arthroscopy. 2011;27:1029–1035. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

