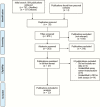
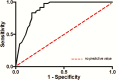
Can Hepatitis C Virus Antigen Testing Replace Ribonucleic Acid Polymearse Chain Reaction Analysis for Detecting Hepatitis C Virus? A Systematic Review
- PMID: 28567430
- PMCID: PMC5445222
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofw252
Can Hepatitis C Virus Antigen Testing Replace Ribonucleic Acid Polymearse Chain Reaction Analysis for Detecting Hepatitis C Virus? A Systematic Review
Abstract
The complexity and cost of current diagnostics for hepatitis C virus (HCV) may act as a prevention to the scale-up of treatment in the developing world. Currently, ribonucleic acid (RNA)-polymerase chain reaction tests are the gold standard. However, there is potential for the use of simpler and cheaper antigen tests to confirm HCV infection in different clinical settings. We evaluated the sensitivity and specificity of antigen assays. This was compared with the reference-standard RNA assays. A subanalysis also assessed Architect core antigen test, which is the only commercially available antigen test on the market. In 24 datasets, evaluating HCV-antigen assays in 8136 samples, the percentage of HCV-antigen positive, HCV-RNA negative was 0.57%. The percentage HCV-antigen negative, HCV-RNA positive was 3.52%. There is strong evidence that antigen detection performs as well as RNA-based assays for HCV management. The use of antigen tests could improve access to HCV care in underresourced healthcare settings.
Keywords: HCV RNA.; HCV antigen; HCV diagnostics.
Figures
References
-
- Cooke GS, Hill AM. Diagnostics for resource-limited settings in the era of interferon-free HCV therapy. J Viral Hepat 2015; 22:459–60. - PubMed
-
- UNITAID. Hepatitis C—Diagnostics Technology Landscape Available at: http://unitaid.org/images/marketdynamics/publications/UNITAID-HCV_Diagno.... Accessed 15 August 2016.
-
- PRISMA. PRISMA Statement Available at: http://www.prisma-statement.org/PRISMAStatement/ Accessed 15 August 2016.
-
- Moses L, Shapiro D, Littenberg B. Combining independent studies of a diagnostic test into a summary ROC curve: data‐analytic approaches and some additional considerations. Stat Med 1993; 12:1293–316. - PubMed
-
- Whiting P, Rutjes A, Westwood ME, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med 2011; 155:529–36. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources