Probing Human Telomeric DNA and RNA Topology and Ligand Binding in a Cellular Model by Using Responsive Fluorescent Nucleoside Probes
- PMID: 28569423
- PMCID: PMC5724660
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201700283
Probing Human Telomeric DNA and RNA Topology and Ligand Binding in a Cellular Model by Using Responsive Fluorescent Nucleoside Probes
Abstract
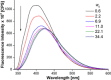
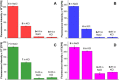
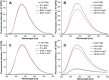
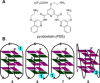
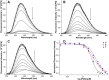
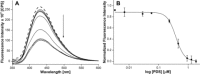
The development of biophysical systems that enable an understanding of the structure and ligand-binding properties of G-quadruplex (GQ)-forming nucleic acid sequences in cells or models that mimic the cellular environment would be highly beneficial in advancing GQ-directed therapeutic strategies. Herein, the establishment of a biophysical platform to investigate the structure and recognition properties of human telomeric (H-Telo) DNA and RNA repeats in a cell-like confined environment by using conformation-sensitive fluorescent nucleoside probes and a widely used cellular model, bis(2-ethylhexyl) sodium sulfosuccinate reverse micelles (RMs), is described. The 2'-deoxy and ribonucleoside probes, composed of a 5-benzofuran uracil base analogue, faithfully report the aqueous micellar core through changes in their fluorescence properties. The nucleoside probes incorporated into different loops of H-Telo DNA and RNA oligonucleotide repeats are minimally perturbing and photophysically signal the formation of respective GQ structures in both aqueous buffer and RMs. Furthermore, these sensors enable a direct comparison of the binding affinity of a ligand to H-Telo DNA and RNA GQ structures in the bulk and confined environment of RMs. These results demonstrate that this combination of a GQ nucleoside probe and easy-to-handle RMs could provide new opportunities to study and devise screening-compatible assays in a cell-like environment to discover GQ binders of clinical potential.
Keywords: G-quadruplexes; fluorescent probes; micelles; nucleosides; telomeric repeats.
© 2017 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures



References
-
- None
-
- Collie G. W., Parkinson G. N., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5867–5892. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

