Interferon-γ derived from cytotoxic lymphocytes directly enhances their motility and cytotoxicity
- PMID: 28569770
- PMCID: PMC5520949
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2017.67
Interferon-γ derived from cytotoxic lymphocytes directly enhances their motility and cytotoxicity
Abstract
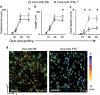
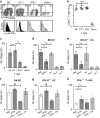
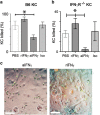
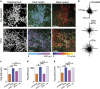
Interferon gamma (IFNγ) is a key moderator of cell-mediated immunity with diverse, mainly pro-inflammatory actions on immunocytes and target tissue. Recent studies have shown it may enhance anti-tumor and antiviral effects of CD8 T cells. Here we investigate the mechanisms by which IFNγ mediates CD8 T-cell cytotoxic function. We show that in vivo, antigen-specific CD8 T cells that produce INFγ are necessary to effect rejection of skin grafts expressing OVA as a transgene in keratinocytes. The ability of CD8 T cells to produce IFNγ enhanced their ability to migrate to the site of antigen-presenting skin cells. By in vivo imaging, we show that CTL motility, particularly speed, during graft rejection was enhanced by locally available IFNγ. We then used a reductionist two-cell model of CTL effectors and keratinocyte targets to investigate the effects of locally available (paracrine) and CTL-producing (autocrine) IFNγ on the motility behavior and killing ability of the CTL. Using live-cell imaging by prolonged time-lapse microscopy of primary effector CD8 T cells and antigen-expressing primary keratinocyte targets, we show that CD8 T-cell cytotoxic function and motility is enhanced by locally available IFNγ. Conversely, deprivation of either autocrine or paracrine IFNγ, or blockade of IFNγ signaling to CTL markedly reduced their cytotoxic function, their kinematics, and effector cell survival. We conclude that in vitro and in vivo, autocrine production of IFNγ by CTL enhances their motility and promotes killing of primary target keratinocytes. The absolute need for local IFNγ to enable cytotoxic CD8 T-cell function is of significance for immunotherapy for chronic viral infection and for cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Martinet L, Garrido I, Filleron T, Le Guellec S, Bellard E, Fournie JJ et al. Human solid tumors contain high endothelial venules: association with T- and B-lymphocyte infiltration and favorable prognosis in breast cancer. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 5678–5687. - PubMed
-
- Bellavance EC, Kohlhapp FJ, Zloza A, O'Sullivan JA, McCracken J, Jagoda MC et al. Development of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cell memory precursor effector cells and antimelanoma memory responses are the result of vaccination and TGF-β blockade during the perioperative period of tumor resection. J Immunol 2011; 186: 3309–3316. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

