Estrogen Receptor Mediates the Radiosensitivity of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 28570501
- PMCID: PMC5466376
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.904810
Estrogen Receptor Mediates the Radiosensitivity of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
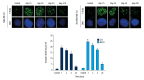
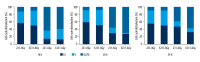
BACKGROUND This study aimed to evaluate differences in the radiosensitivities of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and luminal-type breast cancer cells and to investigate the effects of estrogen receptor (ER) expression on the biological behaviors of the cells. MATERIAL AND METHODS Colony-forming assays were performed to detect differences in radiosensitivities in breast cancer cell lines. Gene transfection technology was used to introduce the expression of ERα in TNBC cells to compare the difference in radiosensitivity between the TNBC cells and ERα transfected cells. CCK-8 assays were used to observe changes in the proliferation of TNBC cells after ERα transfection. Immunofluorescence was used to detect the number of γH2AX foci in nuclei. Flow cytometry was used to detect changes in cell cycle distribution and apoptosis. Western blotting was used to detect changes in autophagy-associated proteins. RESULTS The radioresistance of the TNBC cell line MDA-MB-231 (231 cells) was greater than that of ERα-positive luminal-type breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Moreover, 231 cell proliferation and radioresistance decreased after ERα transfection. Interestingly, ERα-transfected 231 cells showed increased double-stranded breaks and delayed repair compared with 231 cells, and ERα-transfected 231 cells showed increased G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis after irradiation compared with those in 231 cells. ERα transfection in 231 cells reduced autophagy-related protein expression, suggesting that autophagy activity decreased in 231 ER-positive cells after irradiation. CONCLUSIONS TNBC cells were more resistant to radiation than luminal-type breast cancer cells. ERα expression may have major roles in modulating breast cancer cell radiosensitivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



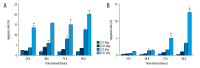
Similar articles
-
Calycosin inhibits triple-negative breast cancer progression through down-regulation of the novel estrogen receptor-α splice variant ER-α30-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2023 Sep;118:154924. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154924. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37393829
-
Downregulation of TMPRSS4 Enhances Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Radiosensitivity Through Cell Cycle and Cell Apoptosis Process Impairment.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2019 Dec 1;20(12):3679-3687. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.12.3679. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2019. PMID: 31870109 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of estrogen receptor-alpha and rearranged during transfection tyrosine kinase is associated with withaferin a-induced apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2011 Oct 6;11:84. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-11-84. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2011. PMID: 21978374 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of AMPK activation by N,N'-diarylurea FND-4b decreases growth and increases apoptosis in triple negative and estrogen-receptor positive breast cancers.PLoS One. 2019 Mar 15;14(3):e0209392. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209392. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30875375 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of melatonin for breast cancer radiation therapy patients.Int J Radiat Biol. 2018 May;94(5):472-477. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2018.1446227. Epub 2018 Mar 14. Int J Radiat Biol. 2018. PMID: 29521142 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased FOXA1 levels induce apoptosis and inhibit proliferation in FOXA1-low expressing basal breast cancer cells.Am J Cancer Res. 2022 Jun 15;12(6):2641-2658. eCollection 2022. Am J Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35812039 Free PMC article.
-
Case - Long-term remission after repeated courses of palliative radiotherapy in a patient with metastatic MiT family translocation renal cell carcinoma.Can Urol Assoc J. 2024 Sep;18(9):E298-E300. doi: 10.5489/cuaj.8771. Can Urol Assoc J. 2024. PMID: 39190179 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Survival comparison between postoperative and preoperative radiotherapy for stage I-III non-inflammatory breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 22;12(1):14288. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18251-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35995985 Free PMC article.
-
The survival benefit of postmastectomy radiotherapy for breast cancer patients with T1-2N1 disease according to molecular subtype.Breast. 2020 Jun;51:40-49. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2020.03.003. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Breast. 2020. PMID: 32200207 Free PMC article.
-
Activated ERK Signaling Is One of the Major Hub Signals Related to the Acquisition of Radiotherapy-Resistant MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 6;22(9):4940. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094940. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34066541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clarke M, Collins R, Darby S, et al. Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival: An overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005;366(9503):2087–106. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Yu X, Chen J, et al. Analysis in early stage triple-negative breast cancer treated with mastectomy without adjuvant radiotherapy: Patterns of failure and prognostic factors. Cancer. 2013;119(13):2366–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

