Oxidized Phospholipids and Risk of Calcific Aortic Valve Disease: The Copenhagen General Population Study
- PMID: 28572160
- PMCID: PMC5551411
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308761
Oxidized Phospholipids and Risk of Calcific Aortic Valve Disease: The Copenhagen General Population Study
Abstract
Objective: Lipoprotein(a) is causally associated with calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD). Lipoprotein(a) carries proinflammatory and procalcific oxidized phospholipids (OxPL). We tested whether the CAVD risk is mediated by the content of OxPL on lipoprotein(a).
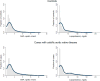
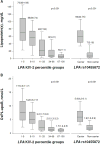
Approach and results: A case-control study was performed within the Copenhagen General Population Study (n=87 980), including 725 CAVD cases (1977-2013) and 1413 controls free of cardiovascular disease. OxPL carried by apoB (apolipoprotein B-100; OxPL-apoB) or apolipoprotein(a) (OxPL-apo(a)) containing lipoproteins, lipoprotein(a) levels, LPA kringle IV type 2 repeat, and rs10455872 genetic variants were measured. OxPL-apoB and OxPL-apo(a) levels correlated with lipoprotein(a) levels among cases (r=0.75 and r=0.95; both P<0.001) and controls (r=0.65 and r=0.93; both P<0.001). OxPL-apoB levels associated with risk of CAVD with odds ratios of 1.2 (95% confidence interval [CI]:1.0-1.6) for 34th to 66th percentile levels, 1.6 (95% CI, 1.2-2.1) for 67th to 90th percentile levels, 2.0 (95% CI, 1.3-3.0) for 91st to 95th percentile levels, and 3.4 (95% CI, 2.1-5.5) for levels >95th percentile, versus levels <34th percentile (trend, P<0.001). Corresponding odds ratios for OxPL-apo(a) were 1.2 (95% CI, 1.0-1.5), 1.2(95% CI, 0.9-1.6), 2.1(95% CI, 1.4-3.1), and 2.9(95% CI, 1.9-4.5; trend, P<0.001) and were similar for lipoprotein(a). LPA genotypes associated with OxPL-apoB, OxPL-apo(a), and lipoprotein(a) levels and explained 34%, 46%, and 39%, respectively, of the total variation in levels. LPA genotypes associated with risk of CAVD; a doubling in genetically determined OxPL-apoB, OxPL-apo(a), and lipoprotein(a) levels associated with odds ratio of CAVD of 1.18 (95% CI, 1.10-1.27), 1.09 (95% CI, 1.05-1.13), and 1.09 (95% CI, 1.05-1.14), respectively, comparable to the corresponding observational estimates of 1.27 (95% CI, 1.16-1.39), 1.13 (95% CI, 1.08-1.18), and 1.11 (95% CI, 1.06-1.17).
Conclusions: OxPL-apoB and OxPL-apo(a) are novel genetic and potentially causal risk factors for CAVD and may explain the association of lipoprotein(a) with CAVD.
Keywords: apolipoproteins B; case-control study; genotype; lipoprotein(a); phospholipids.
© 2017 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures



Comment in
-
OxPL: Elusive Risk Factor in Calcific Aortic Valve Disease or Another Piece of the Puzzle?Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Aug;37(8):1425-1427. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309719. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28747455 No abstract available.
References
-
- Thanassoulis G, Campbell CY, Owens DS, Smith JG, Smith AV, Peloso GM, Kerr KF, Pechlivanis S, Budoff MJ, Harris TB, Malhotra R, O’Brien KD, Kamstrup PR, Nordestgaard BG, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, et al. Genetic associations with valvular calcification and aortic stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:503–512. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kamstrup PR, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, Nordestgaard BG. Elevated lipoprotein(a) and risk of aortic valve stenosis in the general population. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:470–477. - PubMed
-
- Arsenault BJ, Boekholdt SM, Dube MP, Rheaume E, Wareham NJ, Khaw KT, Sandhu MS, Tardif JC. Lipoprotein(a) levels, genotype, and incident aortic valve stenosis: a prospective Mendelian randomization study and replication in a case-control cohort. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2014;7:304–310. - PubMed
-
- Bergmark C, Dewan A, Orsoni A, Merki E, Miller ER, Shin MJ, Binder CJ, Horkko S, Krauss RM, Chapman MJ, Witztum JL, Tsimikas S. A novel function of lipoprotein [a] as a preferential carrier of oxidized phospholipids in human plasma. J Lipid Res. 2008;49:2230–2239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

