Developments in therapy with monoclonal antibodies and related proteins
- PMID: 28572223
- PMCID: PMC6297577
- DOI: 10.7861/clinmedicine.17-3-220
Developments in therapy with monoclonal antibodies and related proteins
Abstract
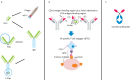
Monoclonal antibody therapeutics have been approved for over 30 targets and diseases, most commonly cancer. Antibodies have become the new backbone of the pharmaceutical industry, which previously relied on small molecules. Compared with small molecules, monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have exquisite target selectivity and hence less toxicity as a result of binding other targets. The clinical value of both mAbs and ligand traps has been proven. New applications of mAbs are being tested and mAbs have now been designed to target two (bi-specific, eg TNF-α and IL-17) or more targets simultaneously, augmenting their therapeutic potential. Because of space limitations and the wide ranging scope of this review there are regrettably, but inevitably, omissions and missing citations. We have chosen to highlight the first successes in inflammatory diseases and cancer, but a broader overview of approved mAbs and related molecules can be found in Table 1.
Keywords: Biologic therapy; cancer; inflammation; monoclonal antibodies; traps.
© Royal College of Physicians 2017. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Köhler G. Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976;6:511–9. - PubMed
-
- Jones PT. Dear PH. Foote J. Neuberger MS. Winter G. Replacing the complementarity-determining regions in a human antibody with those from a mouse. Nature. 1986;321:522–5. - PubMed
-
- Burnet FM. Immunological recognition of self. Science. 1961;133:307–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

